Leading with AI: Strategic Decision Making in the Age of Human-Analogue Machines
The Atomic Human Perspective for Banking Transformation
Neil D. Lawrence
Leading with AI Programme, Cambridge Judge Business School
Introduction: The Age of Human-Analogue Machines
Henry Ford’s Faster Horse

The Atomic Human
Understanding Human vs Machine Intelligence

O M D P C F B V
H G J Q Z Y X K W
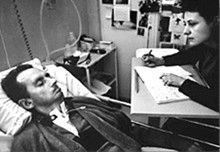
Bauby and Shannon

|

|
|
|
|

|
|
|
bits/min
|
billions
|
2000
|
6
|
|
billion
calculations/s |
~100
|
a billion
|
a billion
|
|
embodiment
|
20 minutes
|
5 billion years
|
15 trillion years
|

The Information Revolution in Banking
New Flow of Information
Evolved Relationship
Evolved Relationship
The Evolution of Decision Making in Banking
Networked Interactions
Bezos memo to Amazon in 2002
The API Mandate
- All teams will henceforth expose their data and functionality through service interfaces.
- Teams must communicate with each other through these interfaces.
- There will be no other form of inter-process communication allowed: no direct linking, no direct reads of another team’s data store, no shared-memory model, no back-doors whatsoever. The only communication allowed is via service interface calls over the network.
- It doesn’t matter what technology they use.
- All service interfaces, without exception, must be designed from the ground up to be externalizable. That is to say, the team must plan and design to be able to expose the interface to developers in the outside world. No exceptions.
Duality of Corporation and Information
- What is less written about is corporate structure.
- This information infrastructure is reflected in the corporation.
- Two pizza teams with devolved autonomy.
- Bound together through corporate culture.
Conway’s Law
Any organization that designs a system (defined broadly) will produce a design whose structure is a copy of the organization’s communication structure.
Conway (n.d.)
Information Topography: How AI Reshapes Banking Decision Making
An Attention Economy
- Human attention will always be a “scarce resource” (See Simon, 1971)
- Humans will never stop being interested in other humans.
- Organisations will keep trying to “capture” the attention economy.
Balancing Centralized Control with Devolved Authority
Question Mark Emails

Executive Sponsorship
- Direct sponsorship from the most senior executive.
- This has a cultural effect as well as a direct effect.
- Bring about through involvement
- develops understanding of capabilities of data science in exec team.
Pathfinder Projects
- In executive context: an important project that is interdepartmental.
- Should involve the CEO, CFO, CIO and data science team (or equivalents).
The Horizon Scandal
|
|
|
|
Complexity in Action
Techno-Inattention Bias in Banking
- Banking organizations develop “techno-inattention bias” - focusing on AI details while missing human dynamics
- The “gorilla” of customer relationships, regulatory compliance, and ethical considerations goes unnoticed
- Institutional inattentional blindness develops when leadership fixates on technical aspects
The Danger for Banking
- AI fascination distracts from nurturing irreplaceable human elements
- Customer trust and relationship management become secondary to technical efficiency
- Regulatory and ethical considerations get overlooked in the rush to automate
Human Attention as the Scarce Resource in Banking
The Attention Economy
Herbert Simon on Information
What information consumes is rather obvious: it consumes the attention of its recipients. Hence a wealth of information creates a poverty of attention …
Simon (1971)
Emulsion: Combining Human and Machine Intelligence in Banking
Attention Reinvestment Cycle
Generative AI as Human-Analogue Machines (HAMs)
Generative AI as HAM
- Generative AI provides us with an “analogue human”
- An information amplifier with a multiplier of 300,000,000.
- Radically changes information infrastructure
- From Conway’s Law: All existing models redundant.
Human-Analogue Machines (HAMs) as Banking Tools
The MONIAC
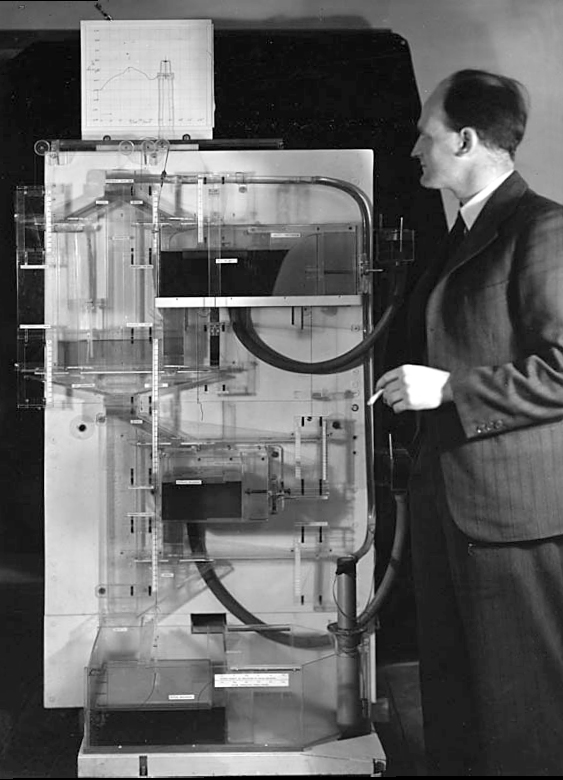
Human Analogue Machine
HAM
The Banking Challenge
- We know everything we’re doing now is wrong.
- We don’t know how it’s wrong.
- “Marconi approach” unlikely to work
The Uncertainty Principle of Human Capital Quantification
Inflation of Human Capital
- Strength in Human Capital double-edged sword.
- Automation creates efficiency.
- But skills risk becoming redundant.
The Business Imperative: People First, Not AI First
AI cannot replace atomic human
Atomic Human Approach for Banking
- Human attention the differentiator.
- Focus on how your human capital needs to adapt.
- People first approach, not AI first.
Superficial Automation
- AI enables automation of surface-level tasks
- Examples: Email writing, document summarization
- Risk of losing deeper value in the process
Hidden Value
- Email writing builds relationships
- Documentation creates institutional memory
- Human pauses enable reflection
The Automation Challenge
- Complex ≠ Complicated
- Speed isn’t always progress
- Augment humans, don’t replace them
- See e.g. ai@cam public dialogues: https://ai.cam.ac.uk/projects/public-dialogues.html
Good Process Drives Purpose

Developing Digital Literacy at Board Level
The Future of Banking: Architecting Human-Machine Collaboration

.
Conclusion
- AI reshapes information flows - understand your information topography
- Balance centralized control and devolved decision-making
- Recognize LLMs as interfaces, not substitutes for human judgment
Strategic Priorities
- Build intelligent accountability into your AI deployments
- Focus on domain expertise leading AI implementation
- Invest in developing institutional character around AI use
- Maintain human judgment in critical decisions
- Prioritize customer trust and relationships

Thanks!
book: The Atomic Human
twitter: @lawrennd
The Atomic Human pages atomic human, the 13 , Le Scaphandre et le papillon (The Diving Bell and the Butterfly) 10–12, Bauby, Jean Dominique 9–11, 18, 90, 99-101, 133, 186, 212–218, 234, 240, 251–257, 318, 368–369, Shannon, Claude 10, 30, 61, 74, 98, 126, 134, 140, 143, 149, 260, 264, 269, 277, 315, 358, 363, Horizon scandal 371, MONIAC 232-233, 266, 343, human-analogue machine (HAMs) 343-347, 359-359, 365-368.
newspaper: Guardian Profile Page
blog posts:
Dan Andrews image of our reflective obsession with AI
Dan Andrews image from Chapter 3