How Engineers Solve Big and Difficult Problems Part 1: The Challenges/Opportunities Presented to Engineers by AI/ML
The Engineer in Society
Complexity in Action
Data Selective Attention Bias
BMI Steps Data
BMI Steps Data Analysis
A Hypothesis as a Liability
“ ‘When someone seeks,’ said Siddhartha, ‘then it easily happens that his eyes see only the thing that he seeks, and he is able to find nothing, to take in nothing. […] Seeking means: having a goal. But finding means: being free, being open, having no goal.’ ”
Hermann Hesse
The Scientific Process

What is Machine Learning?
What is Machine Learning?
\[ \text{data} + \text{model} \stackrel{\text{compute}}{\rightarrow} \text{prediction}\]
- data : observations, could be actively or passively acquired (meta-data).
- model : assumptions, based on previous experience (other data! transfer learning etc), or beliefs about the regularities of the universe. Inductive bias.
- prediction : an action to be taken or a categorization or a quality score.
- Royal Society Report: Machine Learning: Power and Promise of Computers that Learn by Example
What is Machine Learning?
\[\text{data} + \text{model} \stackrel{\text{compute}}{\rightarrow} \text{prediction}\]
- To combine data with a model need:
- a prediction function \(f(\cdot)\) includes our beliefs about the regularities of the universe
- an objective function \(E(\cdot)\) defines the cost of misprediction.
Machine Learning
- Driver of two different domains:
- Data Science: arises from the fact that we now capture data by happenstance.
- Artificial Intelligence: emulation of human behaviour.
- Connection: Internet of Things
Machine Learning
- Driver of two different domains:
- Data Science: arises from the fact that we now capture data by happenstance.
- Artificial Intelligence: emulation of human behaviour.
- Connection: Internet of
Things
Machine Learning
- Driver of two different domains:
- Data Science: arises from the fact that we now capture data by happenstance.
- Artificial Intelligence: emulation of human behaviour.
- Connection: Internet of People
What does Machine Learning do?
- ML Automates through Data
- Strongly related to statistics.
- Field underpins revolution in data science and AI
- With AI:
- logic, robotics, computer vision, language, speech
- With Data Science:
- databases, data mining, statistics, visualization, software systems
Evolved Relationship with Information
New Flow of Information
Evolved Relationship
Evolved Relationship
Data Science Africa is a bottom up initiative for capacity building in data science, machine learning and AI on the African continent
Example: Prediction of Malaria Incidence in Uganda
- Work with Ricardo Andrade Pacheco, John Quinn and Martin Mubangizi (Makerere University, Uganda)
- See AI-DEV Group.
- See UN Global Pulse Disease Outbreaks Site
Malaria Prediction in Uganda
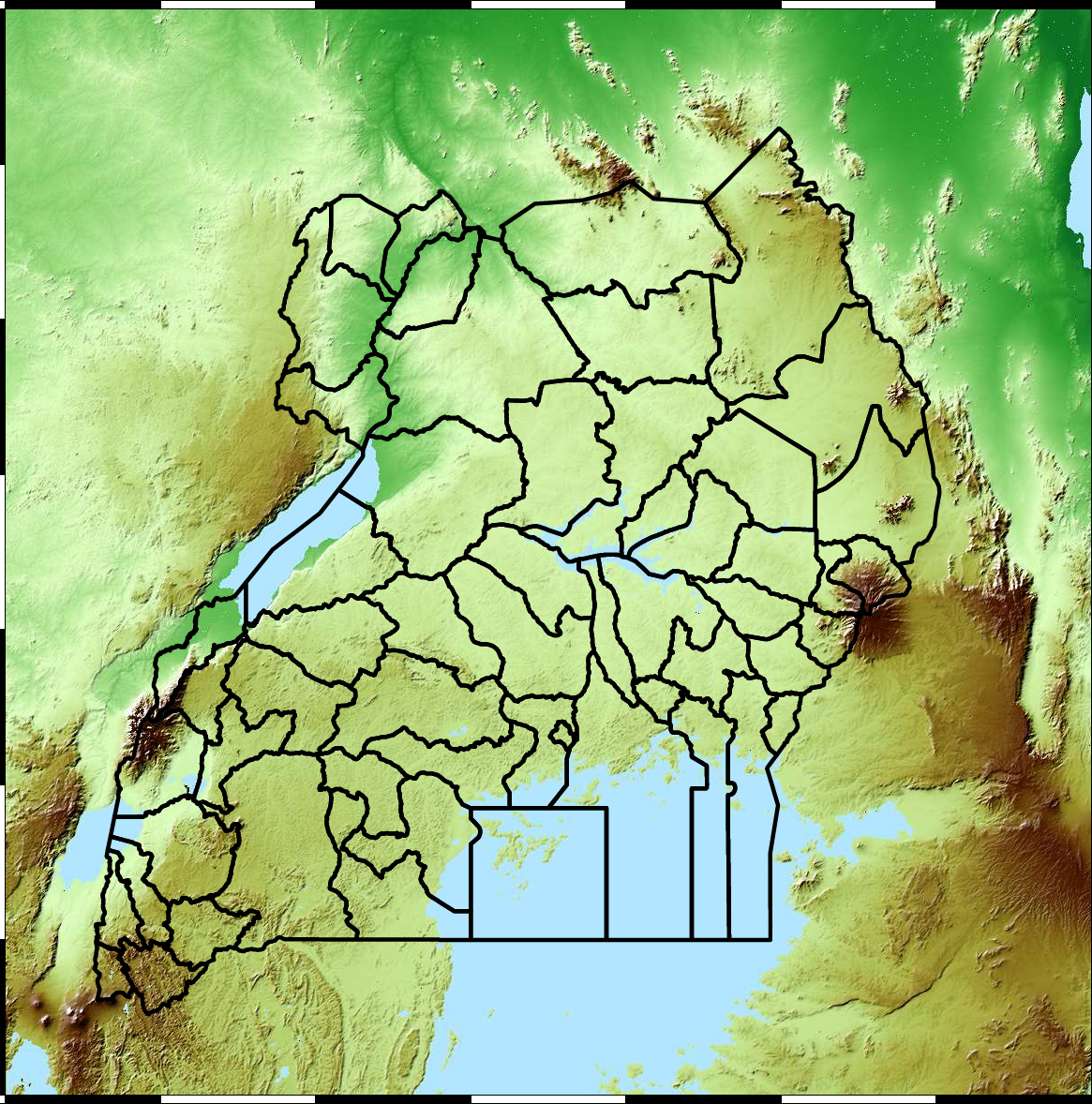
Tororo District
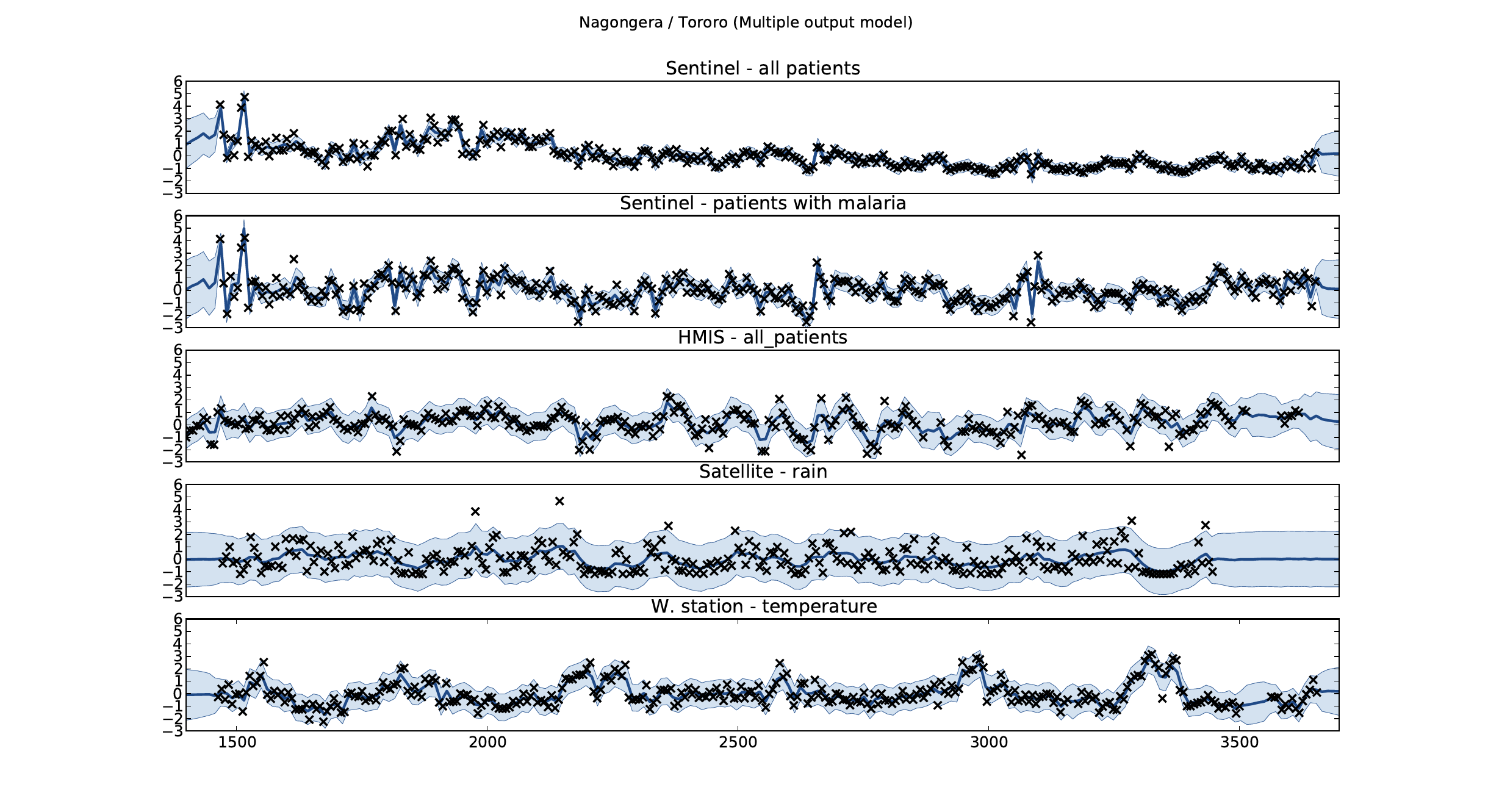
Malaria Prediction in Nagongera (Sentinel Site)
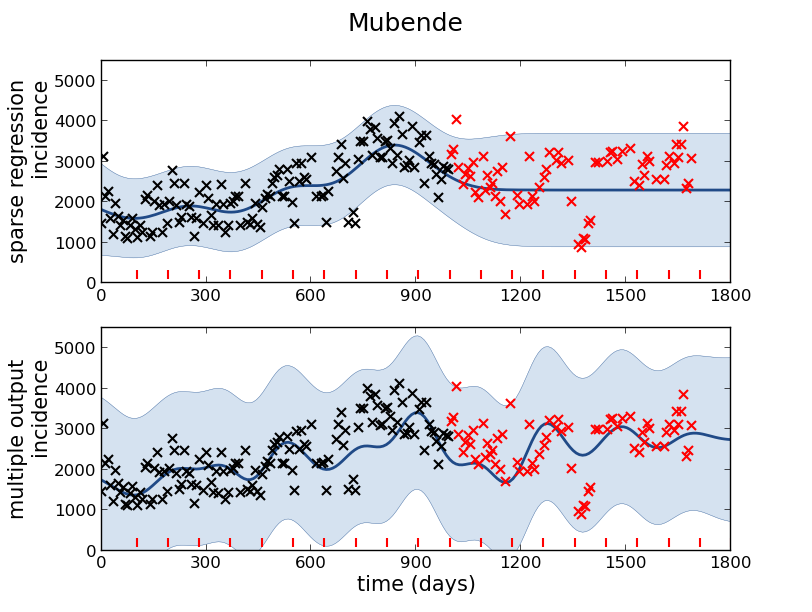
Mubende District
Malaria Prediction in Uganda
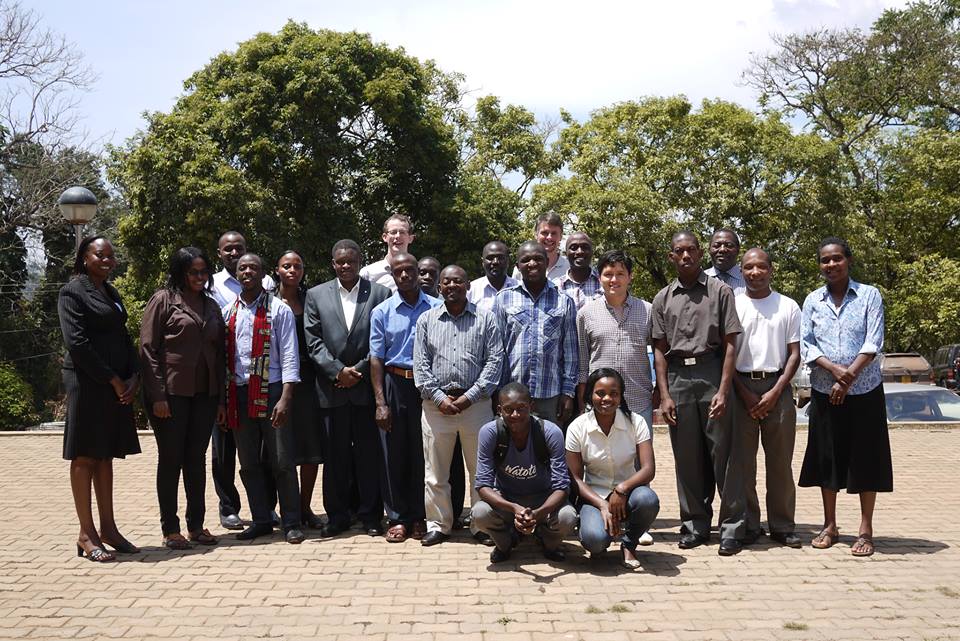
GP School at Makerere

Kabarole District
Early Warning System
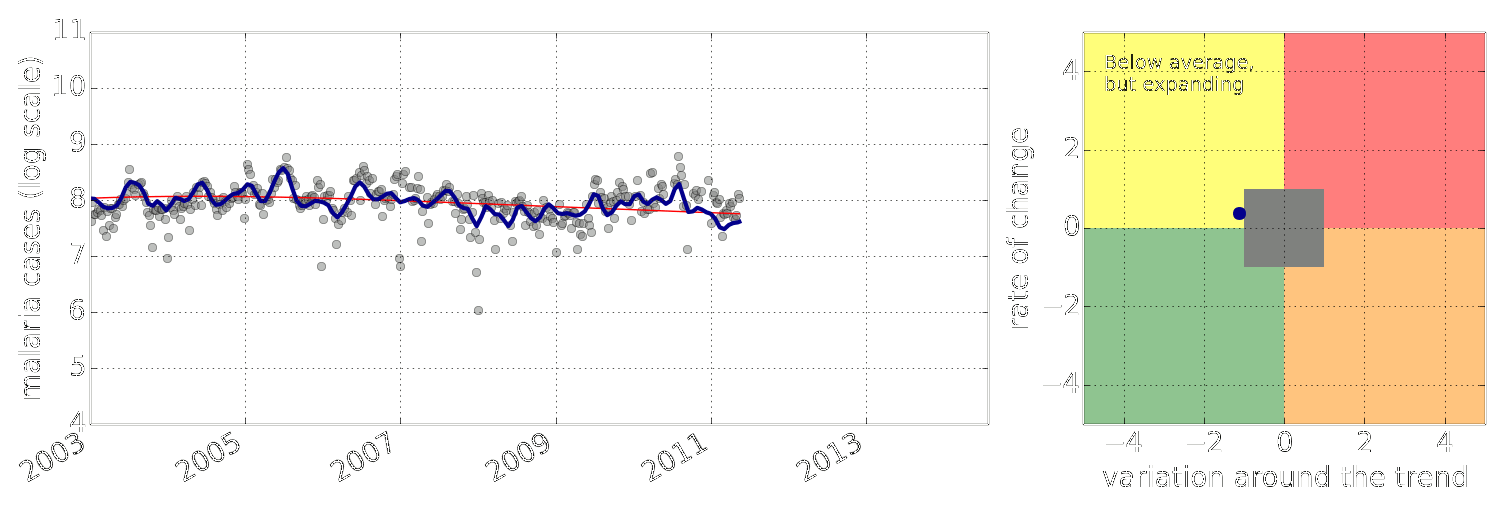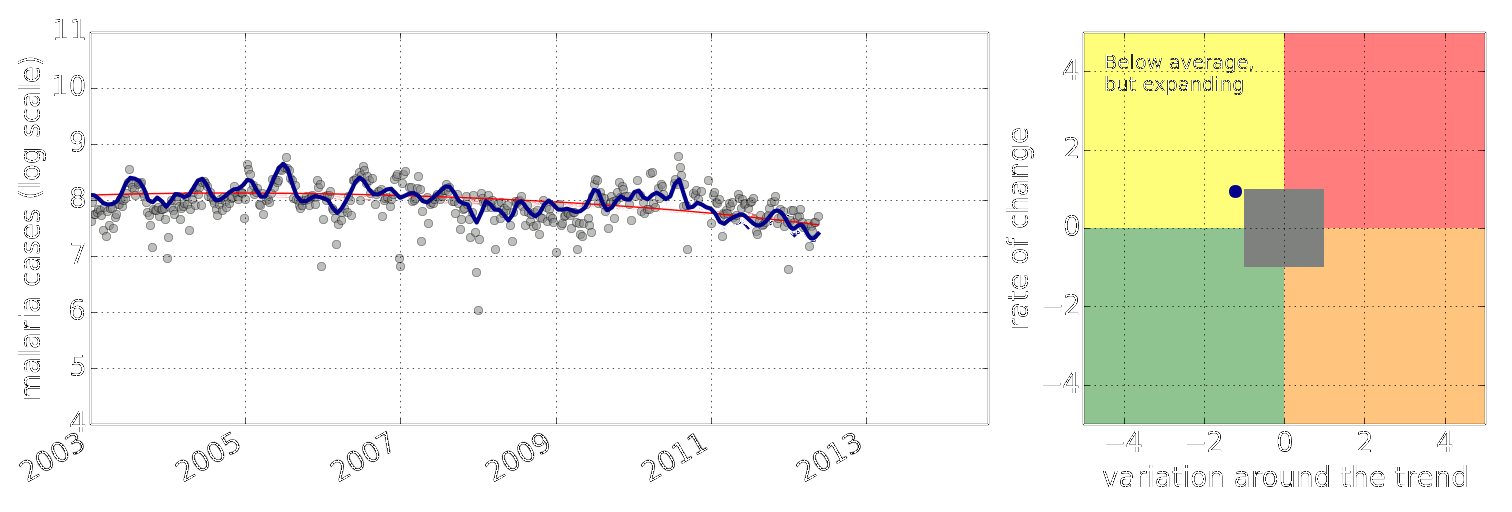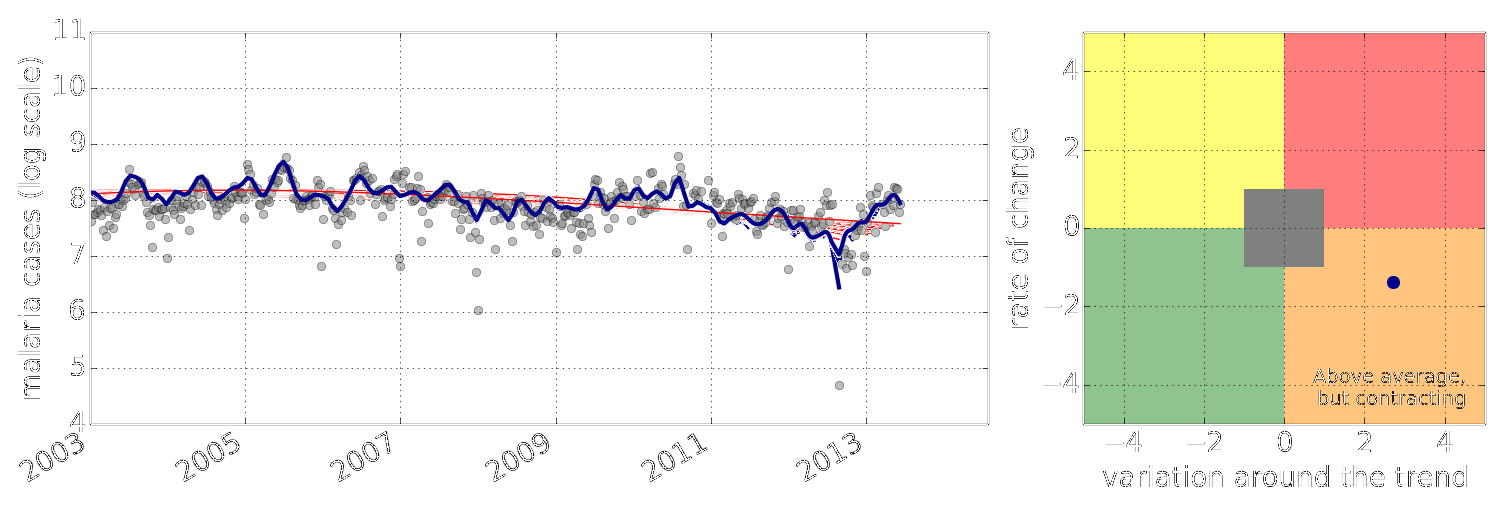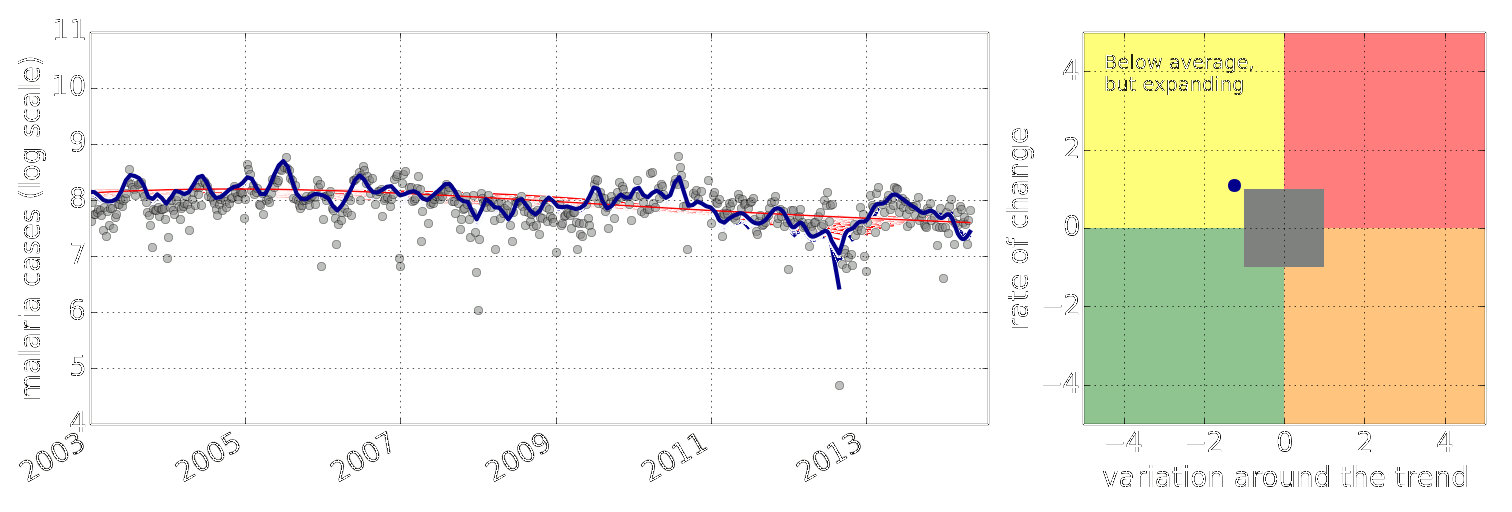
Early Warning Systems
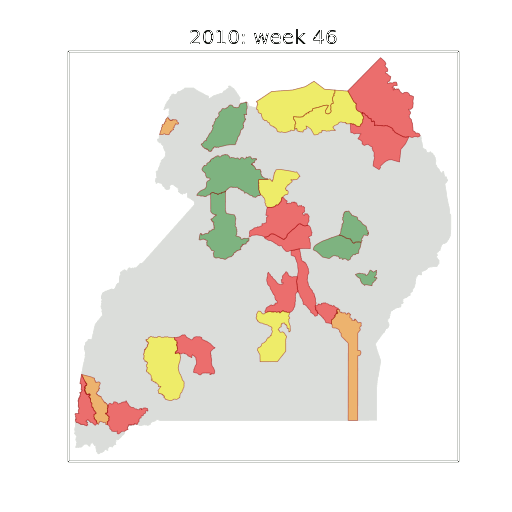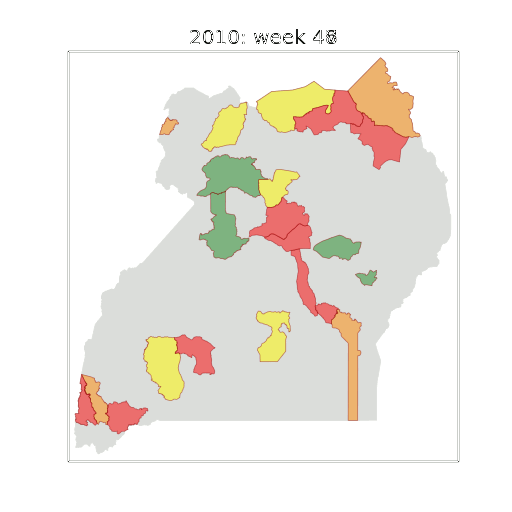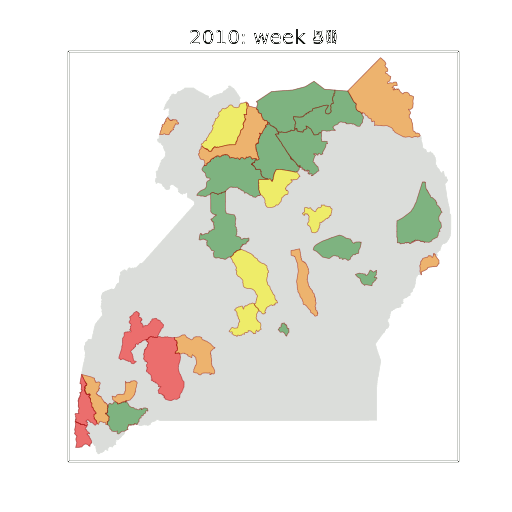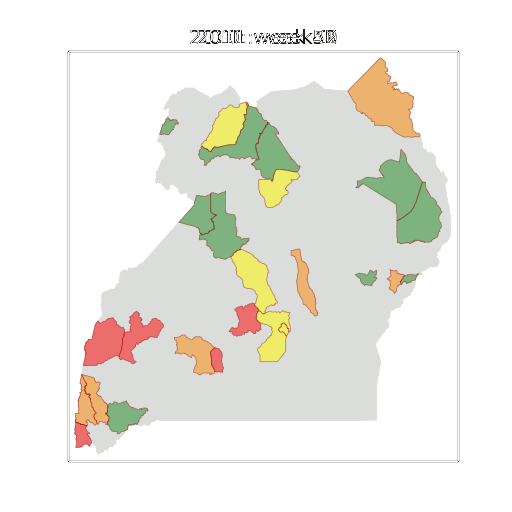
Thanks!
book: The Atomic Human
twitter: @lawrennd
podcast: The Talking Machines
Guardian article on How African can benefit from the data revolution
Guardian article on Data Science Africa
blog posts: