The Atomic Human
Abstract
A vital perspective is missing from the discussions we’re having about Artificial Intelligence: what does it mean for our identity?
Our fascination with AI stems from the perceived uniqueness of human intelligence. We believe it’s what differentiates us. Fears of AI not only concern how it invades our digital lives, but also the implied threat of an intelligence that displaces us from our position at the centre of the world.
Atomism, proposed by Democritus, suggested it was impossible to continue dividing matter down into ever smaller components: eventually we reach a point where a cut cannot be made (the Greek for uncuttable is ‘atom’). In the same way, by slicing away at the facets of human intelligence that can be replaced by machines, AI uncovers what is left: an indivisible core that is the essence of humanity.
I’ll contrast our own (evolved, locked-in, embodied) intelligence with the capabilities of machine intelligence and speculate on what it means for our future.
Henry Ford’s Faster Horse


Figure: A 1925 Ford Model T built at Henry Ford’s Highland Park Plant in Dearborn, Michigan. This example now resides in Australia, owned by the founder of FordModelT.net. From https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:1925_Ford_Model_T_touring.jpg
It’s said that Henry Ford’s customers wanted a “a faster horse”. If Henry Ford was selling us artificial intelligence today, what would the customer call for, “a smarter human”? That’s certainly the picture of machine intelligence we find in science fiction narratives, but the reality of what we’ve developed is much more mundane.
Car engines produce prodigious power from petrol. Machine intelligences deliver decisions derived from data. In both cases the scale of consumption enables a speed of operation that is far beyond the capabilities of their natural counterparts. Unfettered energy consumption has consequences in the form of climate change. Does unbridled data consumption also have consequences for us?
If we devolve decision making to machines, we depend on those machines to accommodate our needs. If we don’t understand how those machines operate, we lose control over our destiny. Our mistake has been to see machine intelligence as a reflection of our intelligence. We cannot understand the smarter human without understanding the human. To understand the machine, we need to better understand ourselves.
The Atomic Human

Figure: The Atomic Eye, by slicing away aspects of the human that we used to believe to be unique to us, but are now the preserve of the machine, we learn something about what it means to be human.
The development of what some are calling intelligence in machines, raises questions around what machine intelligence means for our intelligence. The idea of the atomic human is derived from Democritus’s atomism.
In the fifth century bce the Greek philosopher Democritus posed a similar question about our physical universe. He imagined cutting physical matter into pieces in a repeated process: cutting a piece, then taking one of the cut pieces and cutting it again so that each time it becomes smaller and smaller. Democritus believed this process had to stop somewhere, that we would be left with an indivisible piece. The Greek word for indivisible is atom, and so this theory was called atomism. This book considers this question, but in a different domain, asking: As the machine slices away portions of human capabilities, are we left with a kernel of humanity, an indivisible piece that can no longer be divided into parts? Or does the human disappear altogether? If we are left with something, then that uncuttable piece, a form of atomic human, would tell us something about our human spirit.
See Lawrence (2024) atomic human, the p. 13.
The Diving Bell and the Butterfly


Figure: The Diving Bell and the Buttefly is the autobiography of Jean Dominique Bauby.
The Diving Bell and the Butterfly is the autobiography of Jean Dominique Bauby. Jean Dominique, the editor of French Elle magazine, suffered a major stroke at the age of 43 in 1995. The stroke paralyzed him and rendered him speechless. He was only able to blink his left eyelid, he became a sufferer of locked in syndrome.
See Lawrence (2024) Le Scaphandre et le papillon (The Diving Bell and the Butterfly) p. 10–12.
O M D P C F B V
H G J Q Z Y X K W

Figure: The ordering of the letters that Bauby used for writing his autobiography.
How could he do that? Well, first, they set up a mechanism where he could scan across letters and blink at the letter he wanted to use. In this way, he was able to write each letter.
It took him 10 months of four hours a day to write the book. Each word took two minutes to write.
Imagine doing all that thinking, but so little speaking, having all those thoughts and so little ability to communicate.
One challenge for the atomic human is that we are all in that situation. While not as extreme as for Bauby, when we compare ourselves to the machine, we all have a locked-in intelligence.
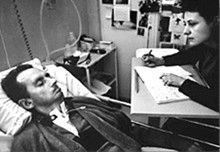

Figure: Jean Dominique Bauby was the Editor in Chief of the French Elle Magazine, he suffered a stroke that destroyed his brainstem, leaving him only capable of moving one eye. Jean Dominique became a victim of locked in syndrome.
Incredibly, Jean Dominique wrote his book after he became locked in. It took him 10 months of four hours a day to write the book. Each word took two minutes to write.
The idea behind embodiment factors is that we are all in that situation. While not as extreme as for Bauby, we all have somewhat of a locked in intelligence.
See Lawrence (2024) Bauby, Jean Dominique p. 9–11, 18, 90, 99-101, 133, 186, 212–218, 234, 240, 251–257, 318, 368–369.
Bauby and Shannon

|

|

Figure: Claude Shannon developed information theory which allows us to quantify how much Bauby can communicate. This allows us to compare how locked in he is to us.
See Lawrence (2024) Shannon, Claude p. 10, 30, 61, 74, 98, 126, 134, 140, 143, 149, 260, 264, 269, 277, 315, 358, 363.
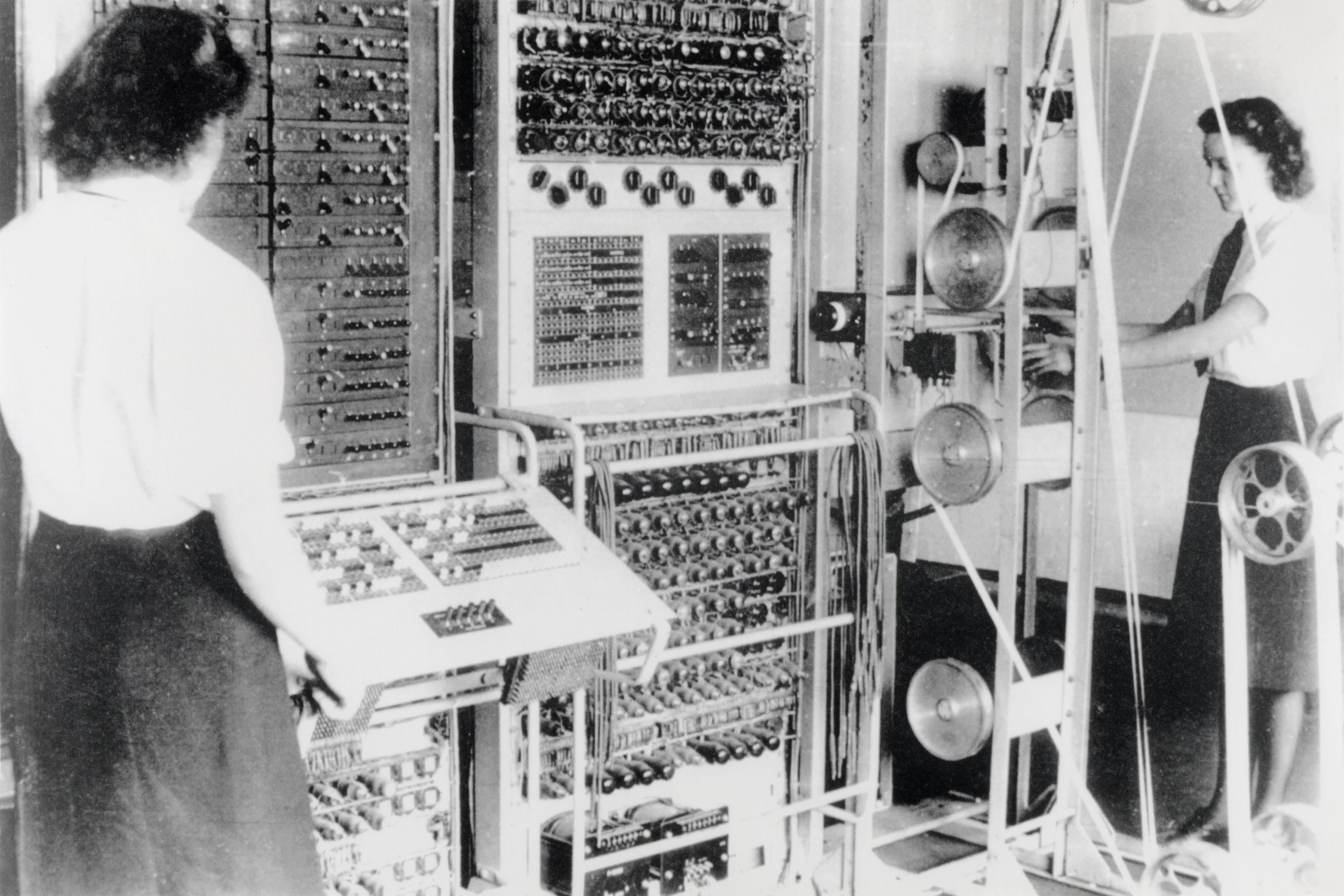

Figure: A Colossus Mark II codebreaking computer being operated by Dorothy Du Boisson (left) and Elsie Booker (right). Colossus was designed by Tommy Flowers, but programmed and operated by groups of Wrens based at Bletchley Park.
In the early hours of 1 June 1944, Tommy Flowers was wading ankle deep in water from a broken pipe, making the final connections to bring Mark 2 Colossus online. Colossus was the world’s first programmable, electronic, digital computer. Four days later, and Eisenhower was reading one of its first decrypts and ordering the invasion of Normandy. Flowers’s machine didn’t just launch an invasion, it launched an intellectual revolution.
See Lawrence (2024) Colossus (computer) p. 76–79, 91, 103, 108, 124, 130, 142–143, 149, 173–176, 199, 231–232, 251, 264, 267, 290, 380.
Embodiment Factors

|
|||
| bits/min | billions | 2000 | 6 |
|
billion calculations/s |
~100 | a billion | a billion |
| embodiment | 20 minutes | 5 billion years | 15 trillion years |

Figure: Embodiment factors are the ratio between our ability to compute and our ability to communicate. Jean Dominique Bauby suffered from locked-in syndrome. The embodiment factors show that relative to the machine we are also locked in. In the table we represent embodiment as the length of time it would take to communicate one second’s worth of computation. For computers it is a matter of minutes, but for a human, whether locked in or not, it is a matter of many millions of years.
Let me explain what I mean. Claude Shannon introduced a mathematical concept of information for the purposes of understanding telephone exchanges.
Information has many meanings, but mathematically, Shannon defined a bit of information to be the amount of information you get from tossing a coin.
If I toss a coin, and look at it, I know the answer. You don’t. But if I now tell you the answer I communicate to you 1 bit of information. Shannon defined this as the fundamental unit of information.
If I toss the coin twice, and tell you the result of both tosses, I give you two bits of information. Information is additive.
Shannon also estimated the average information associated with the English language. He estimated that the average information in any word is 12 bits, equivalent to twelve coin tosses.
So every two minutes Bauby was able to communicate 12 bits, or six bits per minute.
This is the information transfer rate he was limited to, the rate at which he could communicate.
Compare this to me, talking now. The average speaker for TEDX speaks around 160 words per minute. That’s 320 times faster than Bauby or around a 2000 bits per minute. 2000 coin tosses per minute.
But, just think how much thought Bauby was putting into every sentence. Imagine how carefully chosen each of his words was. Because he was communication constrained he could put more thought into each of his words. Into thinking about his audience.
So, his intelligence became locked in. He thinks as fast as any of us, but can communicate slower. Like the tree falling in the woods with no one there to hear it, his intelligence is embedded inside him.
Two thousand coin tosses per minute sounds pretty impressive, but this talk is not just about us, it’s about our computers, and the type of intelligence we are creating within them.
So how does two thousand compare to our digital companions? When computers talk to each other, they do so with billions of coin tosses per minute.
Let’s imagine for a moment, that instead of talking about communication of information, we are actually talking about money. Bauby would have 6 dollars. I would have 2000 dollars, and my computer has billions of dollars.
The internet has interconnected computers and equipped them with extremely high transfer rates.
However, by our very best estimates, computers actually think slower than us.
How can that be? You might ask, computers calculate much faster than me. That’s true, but underlying your conscious thoughts there are a lot of calculations going on.
Each thought involves many thousands, millions or billions of calculations. How many exactly, we don’t know yet, because we don’t know how the brain turns calculations into thoughts.
Our best estimates suggest that to simulate your brain a computer would have to be as large as the UK Met Office machine here in Exeter. That’s a 250 million pound machine, the fastest in the UK. It can do 16 billion billon calculations per second.
It simulates the weather across the word every day, that’s how much power we think we need to simulate our brains.
So, in terms of our computational power we are extraordinary, but in terms of our ability to explain ourselves, just like Bauby, we are locked in.
For a typical computer, to communicate everything it computes in one second, it would only take it a couple of minutes. For us to do the same would take 15 billion years.
If intelligence is fundamentally about processing and sharing of information. This gives us a fundamental constraint on human intelligence that dictates its nature.
I call this ratio between the time it takes to compute something, and the time it takes to say it, the embodiment factor (Lawrence, 2017). Because it reflects how embodied our cognition is.
If it takes you two minutes to say the thing you have thought in a second, then you are a computer. If it takes you 15 billion years, then you are a human.
Bandwidth Constrained Conversations

Figure: Conversation relies on internal models of other individuals.

Figure: Misunderstanding of context and who we are talking to leads to arguments.
Embodiment factors imply that, in our communication between humans, what is not said is, perhaps, more important than what is said. To communicate with each other we need to have a model of who each of us are.
To aid this, in society, we are required to perform roles. Whether as a parent, a teacher, an employee or a boss. Each of these roles requires that we conform to certain standards of behaviour to facilitate communication between ourselves.
Control of self is vitally important to these communications.
The high availability of data available to humans undermines human-to-human communication channels by providing new routes to undermining our control of self.
The consequences between this mismatch of power and delivery are to be seen all around us. Because, just as driving an F1 car with bicycle wheels would be a fine art, so is the process of communication between humans.
If I have a thought and I wish to communicate it, I first need to have a model of what you think. I should think before I speak. When I speak, you may react. You have a model of who I am and what I was trying to say, and why I chose to say what I said. Now we begin this dance, where we are each trying to better understand each other and what we are saying. When it works, it is beautiful, but when mis-deployed, just like a badly driven F1 car, there is a horrible crash, an argument.
Sistine Chapel Ceiling
Shortly before I first moved to Cambridge, my girlfriend (now my wife) took me to the Sistine Chapel to show me the recently restored ceiling.
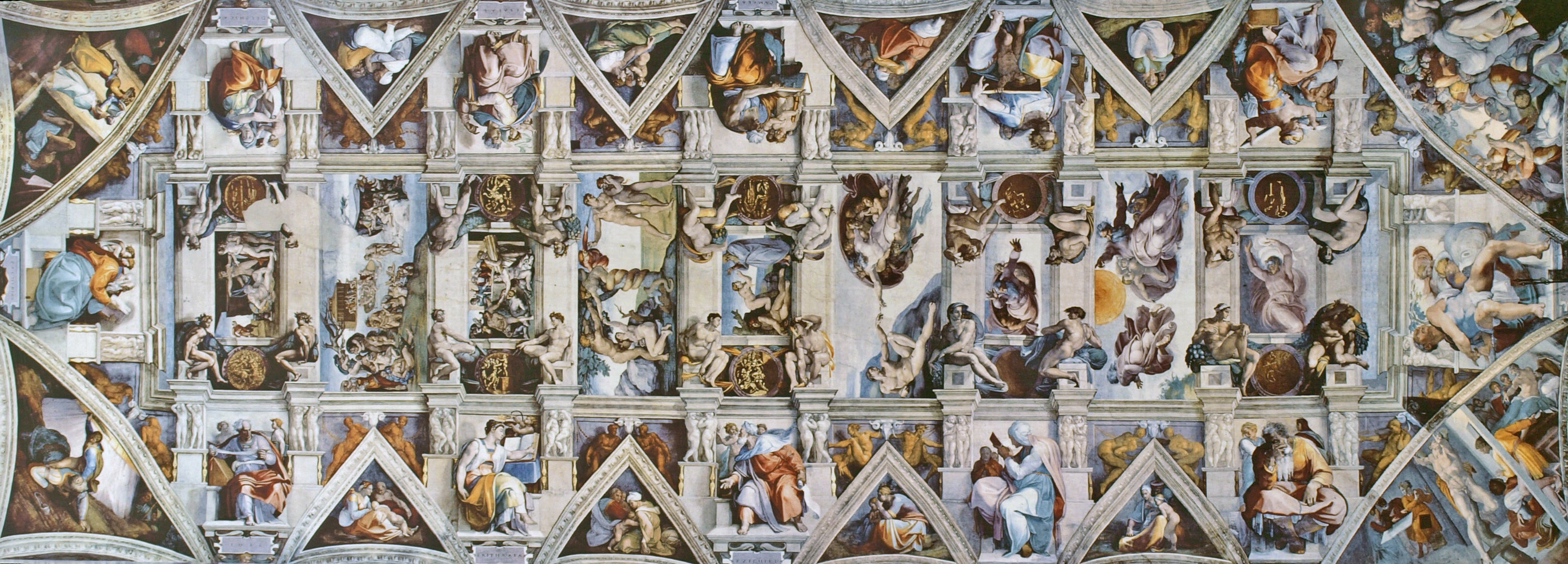


Figure: The ceiling of the Sistine Chapel.
When we got to Cambridge, we both attended Patrick Boyde’s talks on chapel. He focussed on both the structure of the chapel ceiling, describing the impression of height it was intended to give, as well as the significance and positioning of each of the panels and the meaning of the individual figures.
The Creation of Adam
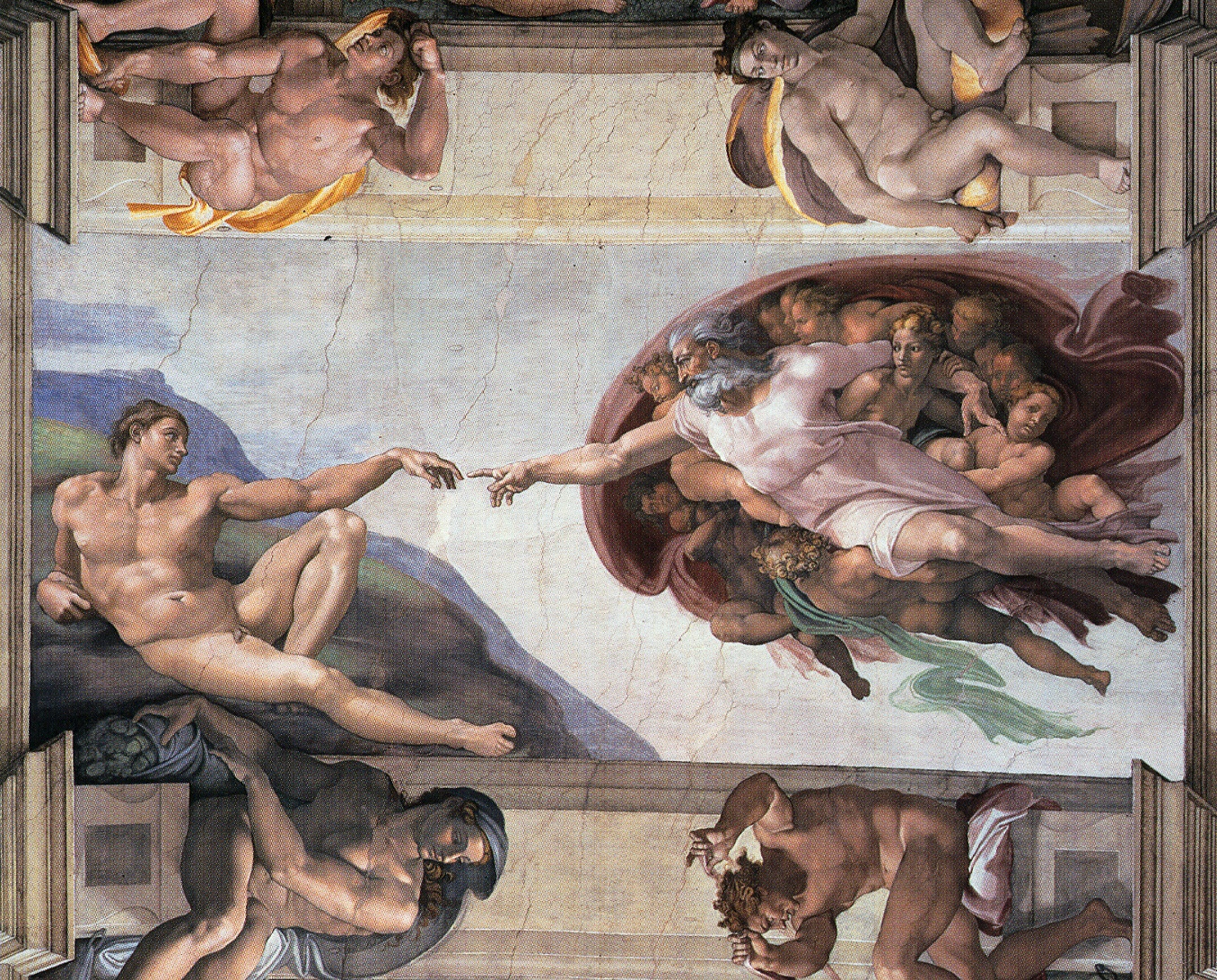


Figure: Photo of Detail of Creation of Man from the Sistine chapel ceiling.
One of the most famous panels is central in the ceiling, it’s the creation of man. Here, God in the guise of a pink-robed bearded man reaches out to a languid Adam.
The representation of God in this form seems typical of the time, because elsewhere in the Vatican Museums there are similar representations.
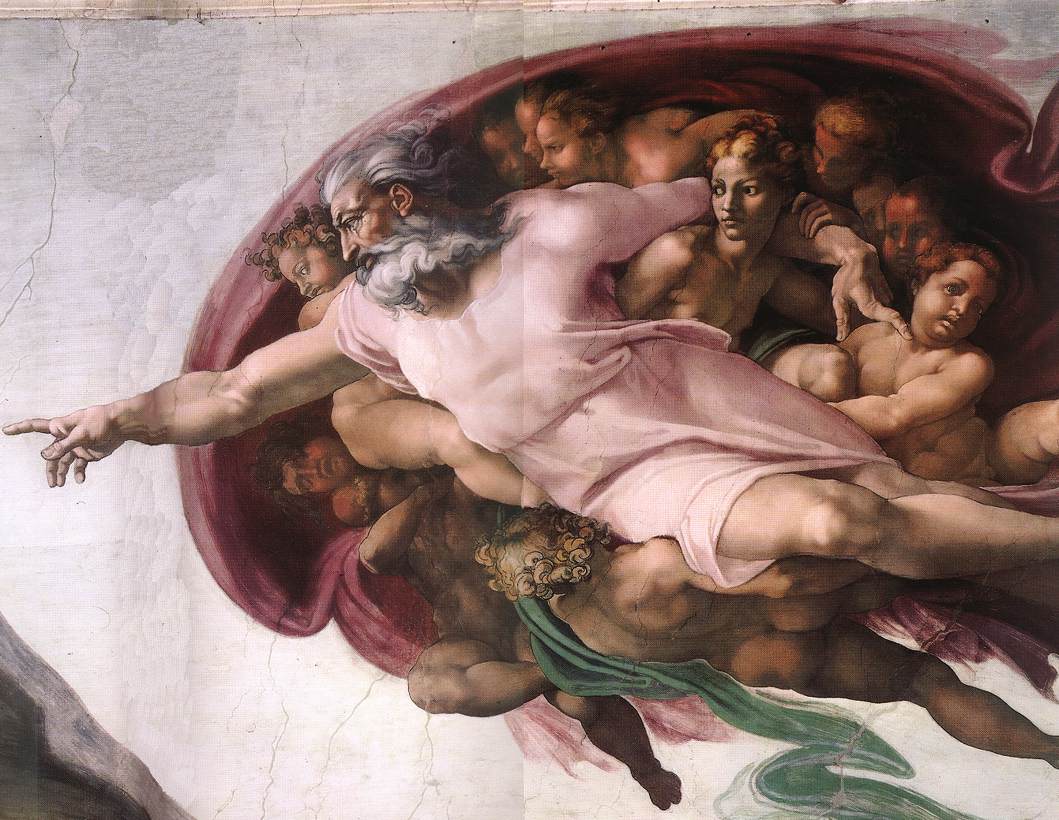


Figure: Photo detail of God.
Photo from https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Michelangelo,_Creation_of_Adam_04.jpg.
My colleague Beth Singler has written about how often this image of creation appears when we talk about AI (Singler, 2020).
See Lawrence (2024) Michelangelo, The Creation of Adam p. 7-9, 31, 91, 105–106, 121, 153, 206, 216, 350.
The way we represent this “other intelligence” in the figure of a Zeus-like bearded mind demonstrates our tendency to embody intelligences in forms that are familiar to us.
Computer Conversations

Figure: Conversation relies on internal models of other individuals.

Figure: Misunderstanding of context and who we are talking to leads to arguments.
Similarly, we find it difficult to comprehend how computers are making decisions. Because they do so with more data than we can possibly imagine.
In many respects, this is not a problem, it’s a good thing. Computers and us are good at different things. But when we interact with a computer, when it acts in a different way to us, we need to remember why.
Just as the first step to getting along with other humans is understanding other humans, so it needs to be with getting along with our computers.
Embodiment factors explain why, at the same time, computers are so impressive in simulating our weather, but so poor at predicting our moods. Our complexity is greater than that of our weather, and each of us is tuned to read and respond to one another.
Their intelligence is different. It is based on very large quantities of data that we cannot absorb. Our computers don’t have a complex internal model of who we are. They don’t understand the human condition. They are not tuned to respond to us as we are to each other.
Embodiment factors encapsulate a profound thing about the nature of humans. Our locked in intelligence means that we are striving to communicate, so we put a lot of thought into what we’re communicating with. And if we’re communicating with something complex, we naturally anthropomorphize them.
We give our dogs, our cats, and our cars human motivations. We do the same with our computers. We anthropomorphize them. We assume that they have the same objectives as us and the same constraints. They don’t.
This means, that when we worry about artificial intelligence, we worry about the wrong things. We fear computers that behave like more powerful versions of ourselves that will struggle to outcompete us.
In reality, the challenge is that our computers cannot be human enough. They cannot understand us with the depth we understand one another. They drop below our cognitive radar and operate outside our mental models.
The real danger is that computers don’t anthropomorphize. They’ll make decisions in isolation from us without our supervision because they can’t communicate truly and deeply with us.
New Flow of Information
Classically the field of statistics focused on mediating the relationship between the machine and the human. Our limited bandwidth of communication means we tend to over-interpret the limited information that we are given, in the extreme we assign motives and desires to inanimate objects (a process known as anthropomorphizing). Much of mathematical statistics was developed to help temper this tendency and understand when we are valid in drawing conclusions from data.

Figure: The trinity of human, data, and computer, and highlights the modern phenomenon. The communication channel between computer and data now has an extremely high bandwidth. The channel between human and computer and the channel between data and human is narrow. New direction of information flow, information is reaching us mediated by the computer. The focus on classical statistics reflected the importance of the direct communication between human and data. The modern challenges of data science emerge when that relationship is being mediated by the machine.
Data science brings new challenges. In particular, there is a very large bandwidth connection between the machine and data. This means that our relationship with data is now commonly being mediated by the machine. Whether this is in the acquisition of new data, which now happens by happenstance rather than with purpose, or the interpretation of that data where we are increasingly relying on machines to summarize what the data contains. This is leading to the emerging field of data science, which must not only deal with the same challenges that mathematical statistics faced in tempering our tendency to over interpret data but must also deal with the possibility that the machine has either inadvertently or maliciously misrepresented the underlying data.
A Six Word Novel
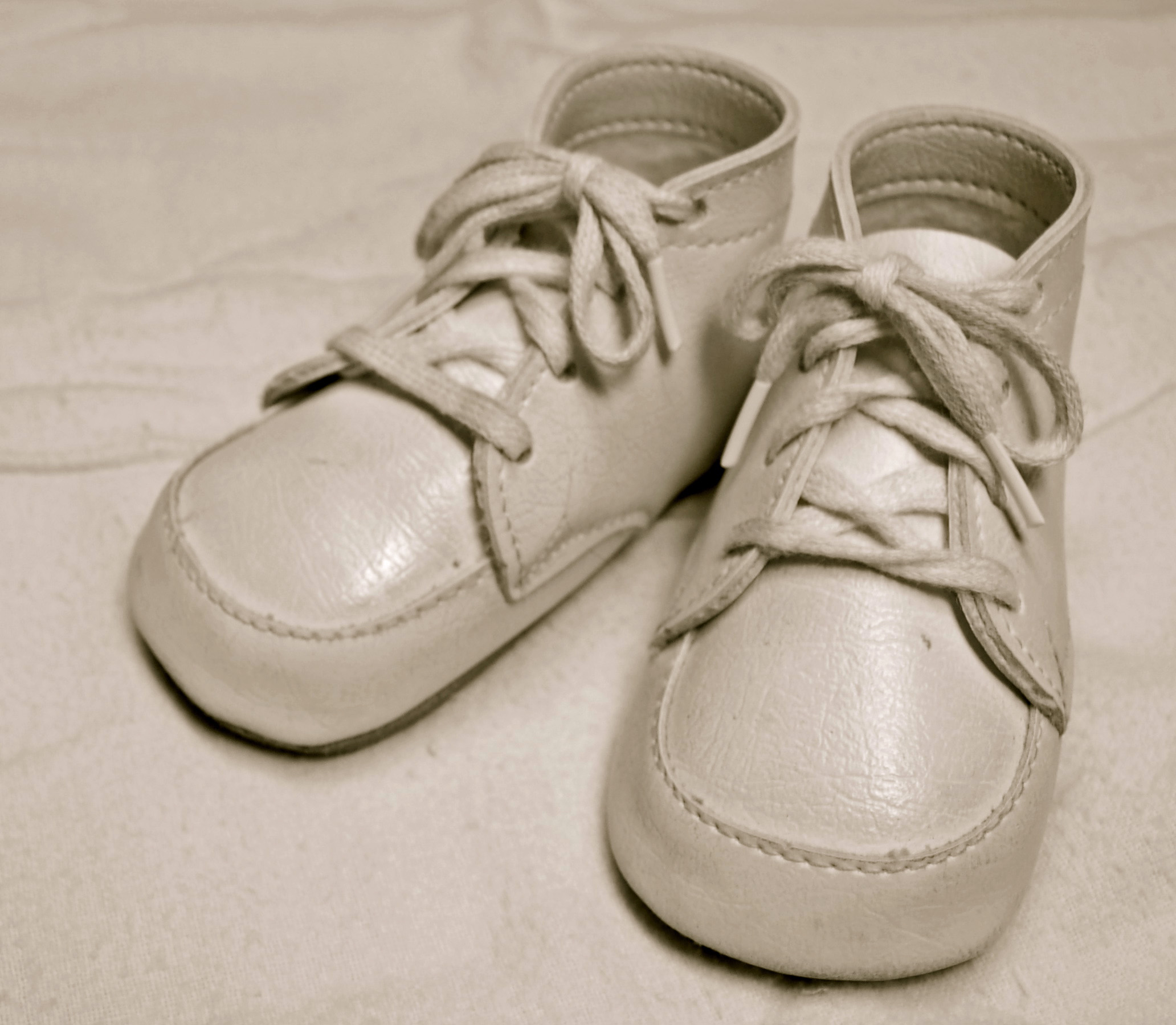


Figure: Consider the six-word novel, apocryphally credited to Ernest Hemingway, “For sale: baby shoes, never worn”. To understand what that means to a human, you need a great deal of additional context. Context that is not directly accessible to a machine that has not got both the evolved and contextual understanding of our own condition to realize both the implication of the advert and what that implication means emotionally to the previous owner.
See Lawrence (2024) baby shoes p. 368.
But this is a very different kind of intelligence than ours. A computer cannot understand the depth of the Ernest Hemingway’s apocryphal six-word novel: “For Sale, Baby Shoes, Never worn”, because it isn’t equipped with that ability to model the complexity of humanity that underlies that statement.
Royal Society Report


Figure: The Royal Society report on Machine Learning was released on 25th April 2017
A useful reference for state of the art in machine learning is the UK Royal Society Report, Machine Learning: Power and Promise of Computers that Learn by Example.
See Lawrence (2024) Royal Society; machine learning review and p. 25, 321, 395.
Public Research


Figure: The Royal Society comissioned public research from Mori as part of the machine learning review.
As is often the cas when members of the public are well convened, they offered sensible opinions about the utility and challenges of machine learning methods.

Figure: One of the questions focussed on machine learning applications.
A range of different scenaios were captured by this qualitative work.
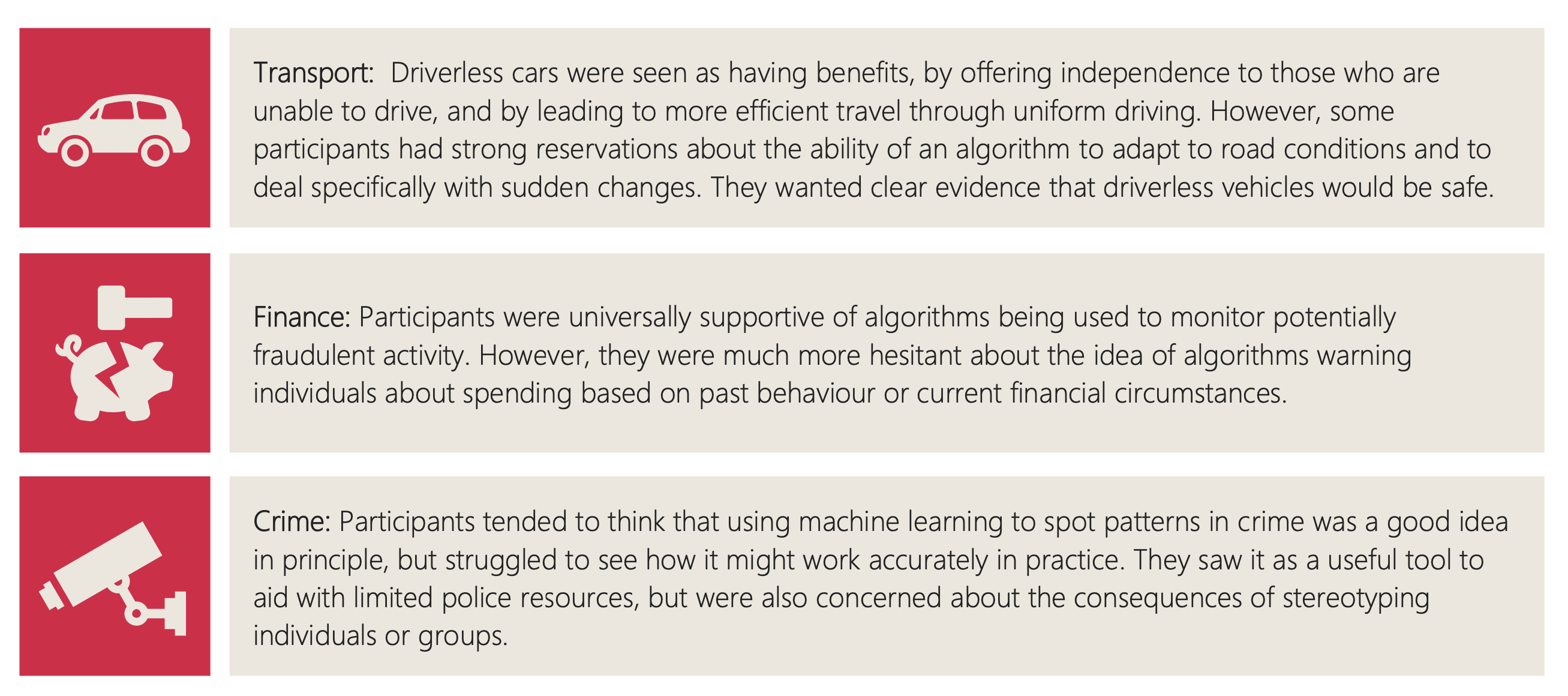

Figure: The public were broadly supportive of a range of application areas.


Figure: But they failed to see the point in AI’s that could produce poetry.
The one scenario where the public were unable to perceive any advantage in machine learning was an example from art, the creation of poetry. This was felt to be a fundamentally human activity that machines could only emulate at best.
Mercutio
It’s ironic that despite the public focus on transport, health, cities, crime and their confusion as to why we might want AI to do art, one area where significant progress has been made is on AIs that can create literature.
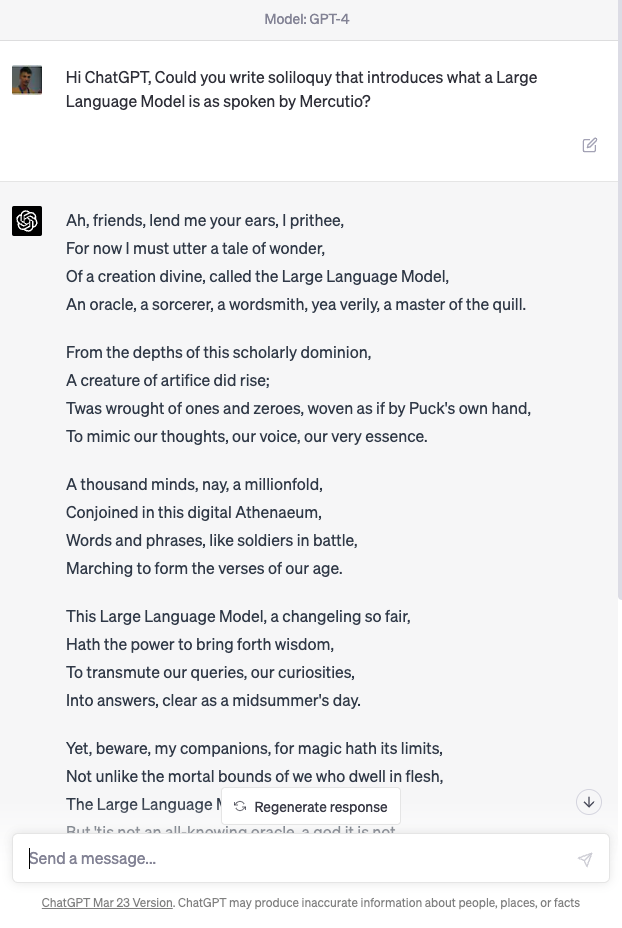

Figure: Despite the public’s desire to see challenges in health, finance, transport, crime solved by machine learning and their skepticism around poetry, one of the problems we have solved seems to be poetry.
User: Hi ChatGPT, Could you write soliloquy that introduces what a Large Language Model is as spoken by Mercutio?
Machine: Ah, friends, lend me your ears, I prithee, For now I must utter a tale of wonder, Of a creation divine, called the Large Language Model, An oracle, a sorcerer, a wordsmith, yea verily, a master of the quill.
From the depths of this scholarly dominion, A creature of artifice did rise; Twas wrought of ones and zeroes, woven as if by Puck’s own hand, To mimic our thoughts, our voice, our very essence.
A thousand minds, nay, a millionfold, Conjoined in this digital Athenaeum, Words and phrases, like soldiers in battle, Marching to form the verses of our age.
This Large Language Model, a changeling so fair, Hath the power to bring forth wisdom, To transmute our queries, our curiosities, Into answers, clear as a midsummer’s day.
Yet, beware, my companions, for magic hath its limits, Not unlike the mortal bounds of we who dwell in flesh, The Large Language Model hath its strengths, But ’tis not an all-knowing oracle, a god it is not.
As Mercutio, your humble servant, doth stand before thee, I marvel at the art and science that hath brought forth this wondrous creation, This Large Language Model, a testament to man’s yearning, To comprehend the world and make meaning of the great tapestry of existence.
In faith, dear friends, let us embrace the magic and beauty of this digital bard, And mayhaps, by its grace, we shall glean some wisdom, As we wander together, hand in hand, Through this boundless realm of knowledge and wonder.
ChatGPT transcript, 14th April 2023.
Revolution
Arguably the information revolution we are experiencing is unprecedented in history. But changes in the way we share information have a long history. Over 5,000 years ago in the city of Uruk, on the banks of the Euphrates, communities which relied on the water to irrigate their corps developed an approach to recording transactions in clay. Eventually the system of recording system became sophisticated enough that their oral histories could be recorded in the form of the first epic: Gilgamesh.
See Lawrence (2024) cuneiform p. 337, 360, 390.


Figure: Chicago Stone, side 2, recording sale of a number of fields, probably from Isin, Early Dynastic Period, c. 2600 BC, black basalt
It was initially developed for people as a record of who owed what to whom, expanding individuals’ capacity to remember. But over a five hundred year period writing evolved to become a tool for literature as well. More pithily put, writing was invented by accountants not poets (see e.g. this piece by Tim Harford).
In some respects today’s revolution is different, because it involves also the creation of stories as well as their curation. But in some fundamental ways we can see what we have produced as another tool for us in the information revolution.
The Future of Professions


Figure: The Future of Professions (Susskind and Susskind, 2015) is a 2015 book focussed on how the next wave of technology revolution is going to effect the professions.
Richard and Daniel Susskind’s 2015 book foresaw that the next wave of automation, artificial intelligence, would have an effect on professional work, information work. And that looks likely to be the case. But professionals are typically well educated and can adapt to changes in their circumstances. For example stocks have already been revolutionised by algorithmic trading, businesses and individuals have adapted to those changes.
Intellectual Debt

Figure: Jonathan Zittrain’s term to describe the challenges of explanation that come with AI is Intellectual Debt.
In the context of machine learning and complex systems, Jonathan Zittrain has coined the term “Intellectual Debt” to describe the challenge of understanding what you’ve created. In the ML@CL group we’ve been foucssing on developing the notion of a data-oriented architecture to deal with intellectual debt (Cabrera et al., 2023).
Zittrain points out the challenge around the lack of interpretability of individual ML models as the origin of intellectual debt. In machine learning I refer to work in this area as fairness, interpretability and transparency or FIT models. To an extent I agree with Zittrain, but if we understand the context and purpose of the decision making, I believe this is readily put right by the correct monitoring and retraining regime around the model. A concept I refer to as “progression testing”. Indeed, the best teams do this at the moment, and their failure to do it feels more of a matter of technical debt rather than intellectual, because arguably it is a maintenance task rather than an explanation task. After all, we have good statistical tools for interpreting individual models and decisions when we have the context. We can linearise around the operating point, we can perform counterfactual tests on the model. We can build empirical validation sets that explore fairness or accuracy of the model.
See Lawrence (2024) intellectual debt p. 84, 85, 349, 365.
Technical Debt
In computer systems the concept of technical debt has been surfaced by authors including Sculley et al. (2015). It is an important concept, that I think is somewhat hidden from the academic community, because it is a phenomenon that occurs when a computer software system is deployed.
Separation of Concerns
To construct such complex systems an approach known as “separation of concerns” has been developed. The idea is that you architect your system, which consists of a large-scale complex task, into a set of simpler tasks. Each of these tasks is separately implemented. This is known as the decomposition of the task.
This is where Jonathan Zittrain’s beautifully named term “intellectual debt” rises to the fore. Separation of concerns enables the construction of a complex system. But who is concerned with the overall system?
Technical debt is the inability to maintain your complex software system.
Intellectual debt is the inability to explain your software system.
It is right there in our approach to software engineering. “Separation of concerns” means no one is concerned about the overall system itself.
See Lawrence (2024) separation of concerns p. 84-85, 103, 109, 199, 284, 371.
See Lawrence (2024) intellectual debt p. 84-85, 349, 365, 376.
The Sorcerer’s Apprentice
See this blog blog post on The Open Society and its AI.
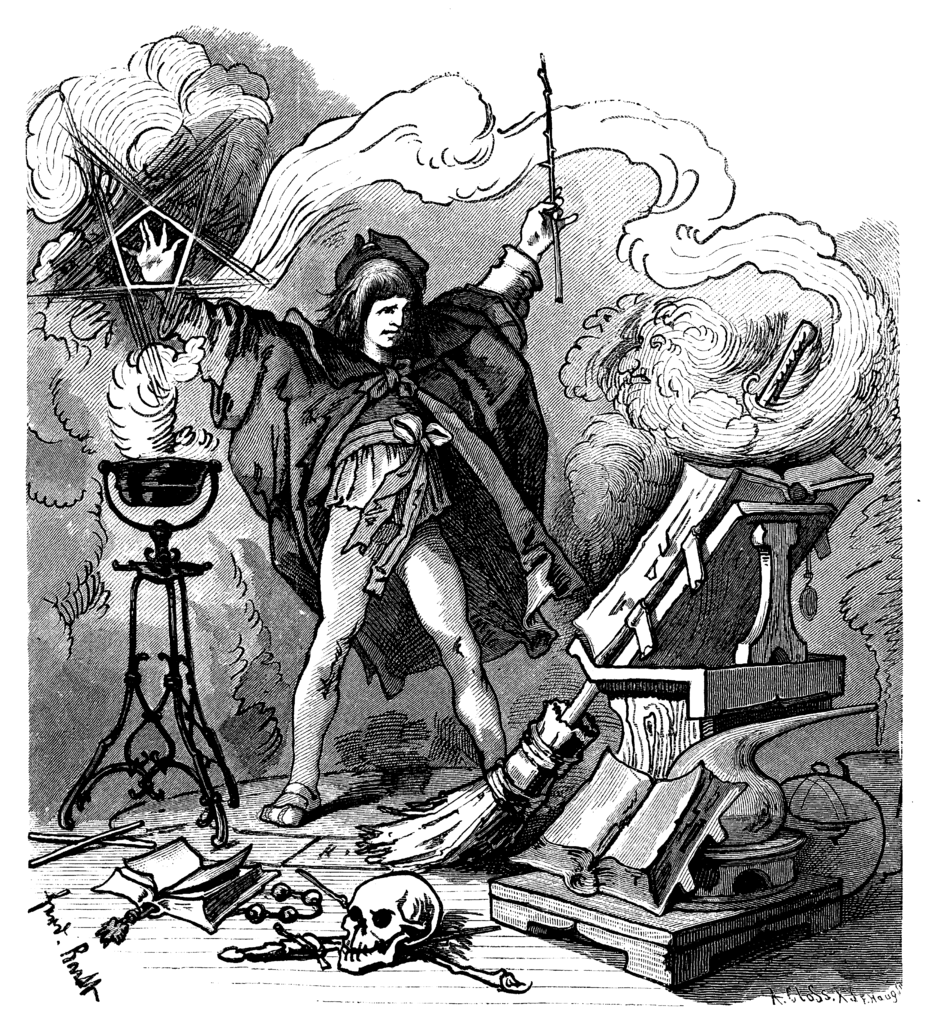


Figure: A young sorcerer learns his masters spells, and deploys them to perform his chores, but can’t control the result.
In Goethe’s poem The Sorcerer’s Apprentice, a young sorcerer learns one of their master’s spells and deploys it to assist in his chores. Unfortunately, he cannot control it. The poem was popularised by Paul Dukas’s musical composition, in 1940 Disney used the composition in the film Fantasia. Mickey Mouse plays the role of the hapless apprentice who deploys the spell but cannot control the results.
When it comes to our software systems, the same thing is happening. The Harvard Law professor, Jonathan Zittrain calls the phenomenon intellectual debt. In intellectual debt, like the sorcerer’s apprentice, a software system is created but it cannot be explained or controlled by its creator. The phenomenon comes from the difficulty of building and maintaining large software systems: the complexity of the whole is too much for any individual to understand, so it is decomposed into parts. Each part is constructed by a smaller team. The approach is known as separation of concerns, but it has the unfortunate side effect that no individual understands how the whole system works. When this goes wrong, the effects can be devastating. We saw this in the recent Horizon scandal, where neither the Post Office or Fujitsu were able to control the accounting system they had deployed, and we saw it when Facebook’s systems were manipulated to spread misinformation in the 2016 US election.
In 2019 Mark Zuckerberg wrote an op-ed in the Washington Post calling for regulation of social media. He was repeating the realisation of Goethe’s apprentice, he had released a technology he couldn’t control. In Goethe’s poem, the master returns, “Besen, besen! Seid’s gewesen” he calls, and order is restored, but back in the real world the role of the master is played by Popper’s open society. Unfortunately, those institutions have been undermined by the very spell that these modern apprentices have cast. The book, the letter, the ledger, each of these has been supplanted in our modern information infrastructure by the computer. The modern scribes are software engineers, and their guilds are the big tech companies. Facebook’s motto was to “move fast and break things”. Their software engineers have done precisely that and the apprentice has robbed the master of his powers. This is a desperate situation, and it’s getting worse. The latest to reprise the apprentice’s role are Sam Altman and OpenAI who dream of “general intelligence” solutions to societal problems which OpenAI will develop, deploy, and control. Popper worried about the threat of totalitarianism to our open societies, today’s threat is a form of information totalitarianism which emerges from the way these companies undermine our institutions.
So, what to do? If we value the open society, we must expose these modern apprentices to scrutiny. Open development processes are critical here, Fujitsu would never have got away with their claims of system robustness for Horizon if the software they were using was open source. We also need to re-empower the professions, equipping them with the resources they need to have a critical understanding of these technologies. That involves redesigning the interface between these systems and the humans that empowers civil administrators to query how they are functioning. This is a mammoth task. But recent technological developments, such as code generation from large language models, offer a route to delivery.
The open society is characterised by institutions that collaborate with each otherin the pragmatic pursuit of solutions to social problems. The large tech companies that have thrived because of the open society are now putting that ecosystem in peril. For the open society to survive it needs to embrace open development practices that enable Popper’s piecemeal social engineers to come back together and chant “Besen, besen! Seid’s gewesen.” Before it is too late for the master to step in and deal with the mess the apprentice has made.
See Lawrence (2024) sorcerer’s apprentice p. 371-374.
The Open Society and its Enemies


Figure: The Open Society and Its Enemies by Karl Popper views liberal democracies as a collection of “piecemeal social engineers” who strive towards better outcomes.
Popper opened the preface to his book (Popper, 1945) with the following words:
If in this book harsh words are spoken about some of the greatest among the intellectual leaders of mankind, my motive is not, I hope, to belittle them. It springs rather from my conviction that, if our civilization is to survive, we must break with the habit of deference to great men. Great men may make great mistakes; and as the book tries to show, some of the greatest leaders of the past supported the perennial attack on freedom and reason.
He had written the book against the background of the second world war, his decision to write it taken on the day the Nazis invaded Austria in March 1938. His book is a reaction to totalitarianism.
For Popper, the ideas of “great men” become totalitarian when imposed on society. He advocates for direct liberal democracy as the only form of government that can allow for institutional change without bloodshed. The open society is one characterized by institutions and individuals that can engage in the practical pursuit of solutions to social and political problems. The institutions are also underpinned by individuals: lawyers, accountants, civil administrators and many more. To Popper it is these “piecemeal social engineers” who offer pragmatic solutions to our society’s political and social challenges.
See Lawrence (2024) Popper, Karl The Open Society and its Enemies p. 371–374.
Coin Pusher
Disruption of society is like a coin pusher, it’s those who are already on the edge who are most likely to be effected by disruption.
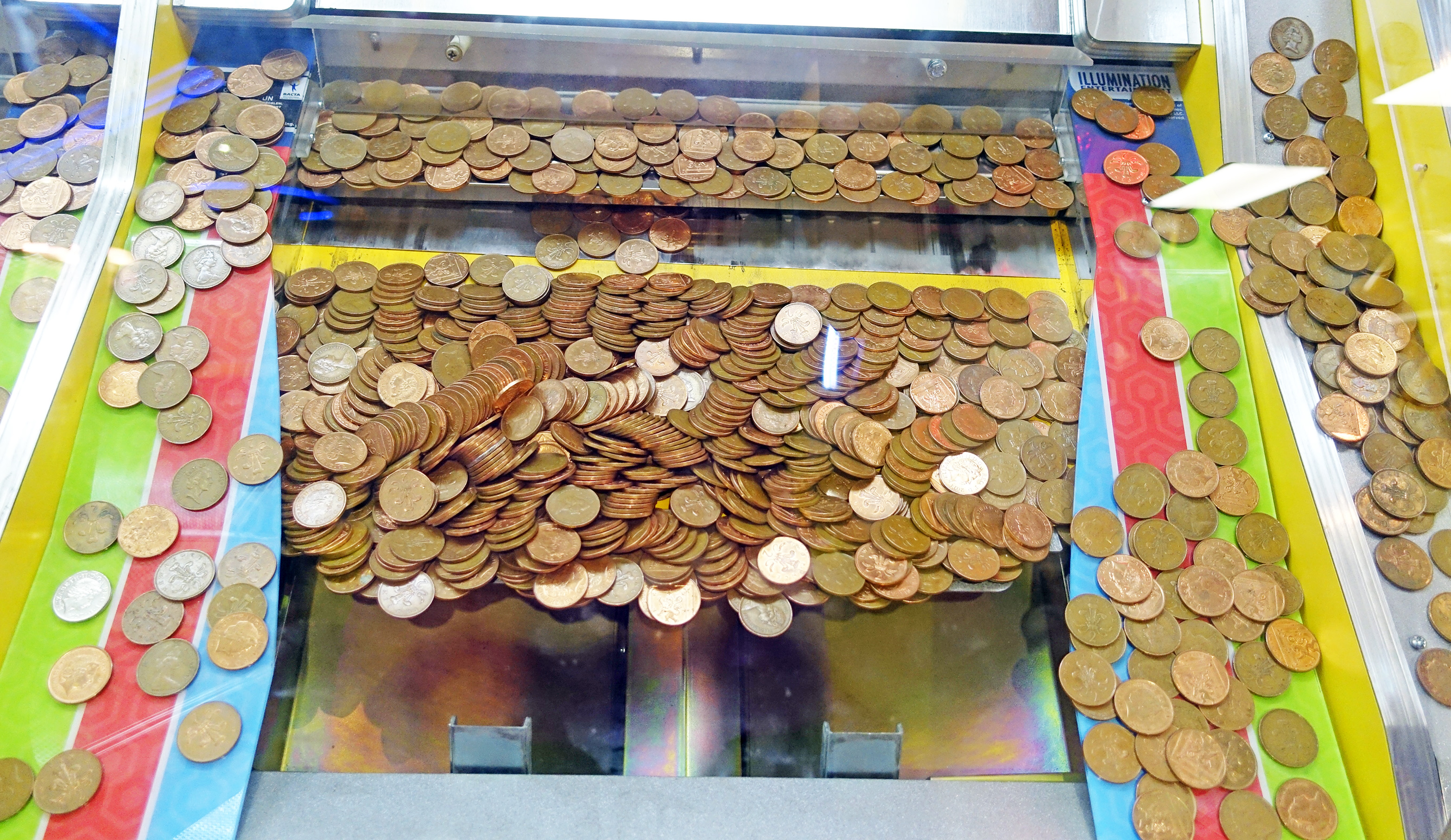


Figure: A coin pusher is a game where coins are dropped into th etop of the machine, and they disrupt those on the existing steps. With any coin drop, many coins move, but it is those on the edge, who are often only indirectly effected, but also most traumatically effected by the change.
One danger of the current hype around ChatGPT is that we are overly focussing on the fact that it seems to have significant effect on professional jobs, people are naturally asking the question “what does it do for my role?”. No doubt, there will be disruption, but the coin pusher hypothesis suggests that that disruption will likely involve movement on the same step. However it is those on the edge already, who are often not working directly in the information economy, who often have less of a voice in the policy conversation who are likely to be most disrupted.
The Horizon Scandal
In the UK we saw these effects play out in the Horizon scandal: the accounting system of the national postal service was computerized by Fujitsu and first installed in 1999, but neither the Post Office nor Fujitsu were able to control the system they had deployed. When it went wrong individual sub postmasters were blamed for the systems’ errors. Over the next two decades they were prosecuted and jailed leaving lives ruined in the wake of the machine’s mistakes.
See Lawrence (2024) Horizon scandal p. 371.
The Code of Hammurabi
The earliest written systems of law come from Babylon. One of them is the code of Hammurabi, named for a Babylonian king who ruled nearly 4,000 years ago.
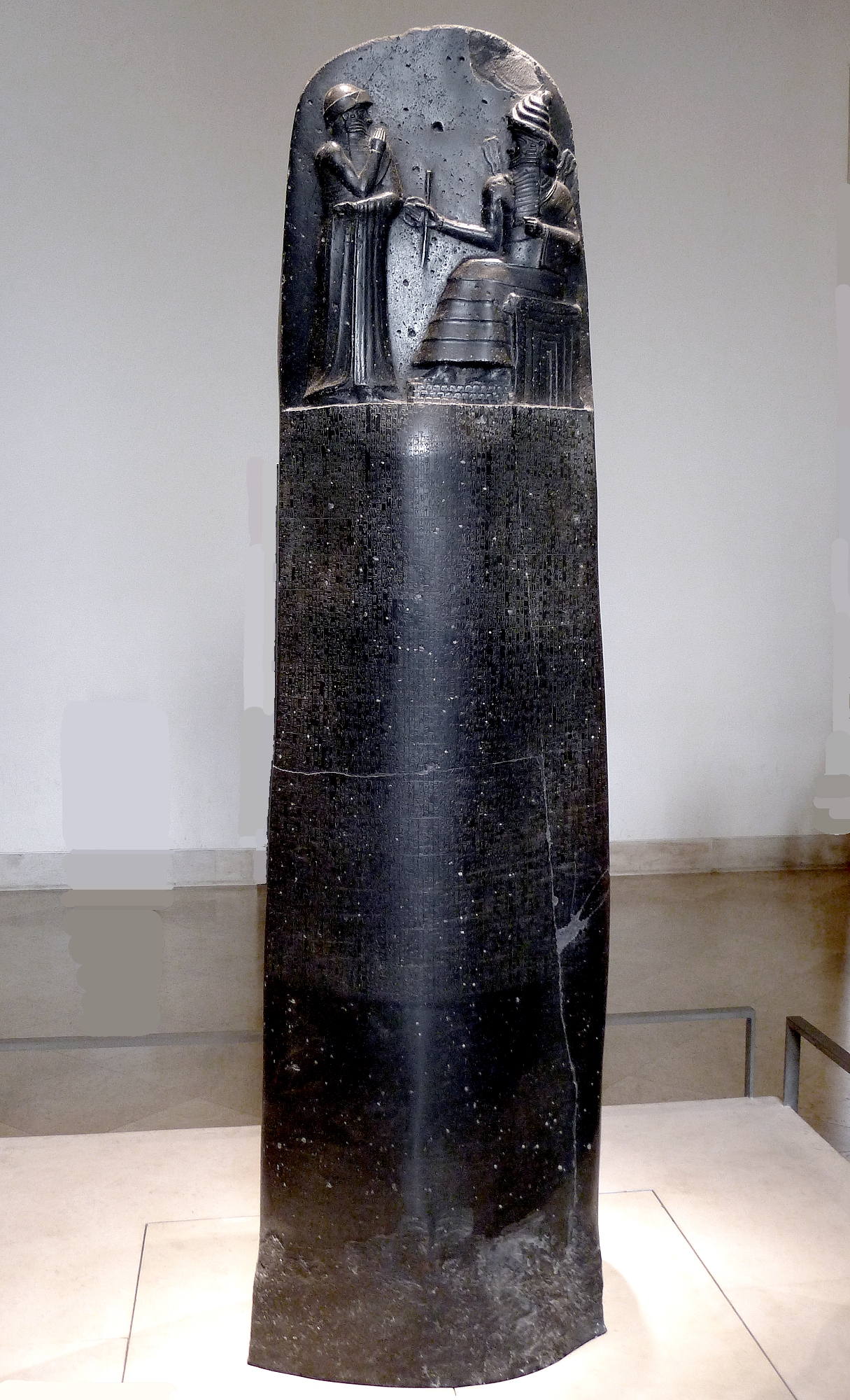


Figure: The code of Hammurabi is estimated to come from around 1750 BC, it is not the first legal codification but one of the best organised. It is written in a dialect of Akkadian. Hammurabi was the sixth king from the first Babylonian dynasty. The code is inscribed on a basalt rock that is over two meters tall.
The second law of the code describes trial by ordeal. The ordeal involved leaping or being thrown in to a river. If an accused survived this then they were acquitted.
See Lawrence (2024) Hammurabi p. 338. See Lawrence (2024) trial by ordeal p. 338-340, 351.
The Trial of Siyatu

Figure: Cuneiform tablet of unknown scribe written between 1250 and 1200 bce, found in Ur, trans. Jonathan Tenney. The text is known as ‘UET 7 11’. It was excavated at the ancient city of Ur and now rests in the Iraq Museum in Baghdad. Oliver R. Gurney (1974), ‘Middle Babylonian legal documents and other texts’, Ur Excavations. Texts 7 (London: The Trustees of the Two Museums). The translation is by my col- league Dr Jonathan Tenney. For more details on the tablet see https://cdli.mpiwg-berlin.mpg.de/artifacts/346976
Jonathan Tenney is an Assyriologist who spends his days reading these ancient texts. His domain of expertise is the city of Nippur, where Gilgamesh built the great gate. The period Jonathan studies is 2,000 years after the reign of Gilgamesh. Through his studies he can give snapshots of life in these cities. One of these snapshots is a trial that took place under Hammurabi’s code. The trial concerned the disappearance of an ox. Cases were presided over by a shakannakku, normally a representative of the king.
Judgement that Adad-šuma-usur, the shakannakku gave:
Regarding the ox that Nergal-aha-iddina loaned to Sin-bununi and then died in the house of Sin-bununi:
If Siyatu the messenger of Nergal-aha-iddina removed the corpse from the house of Sin-bununi and then threw it to a dog, may Sin-bununi be cleared [of wrongdoing by the ordeal] and the man of Nergal-aha-iddina [Siyatu] be proved guilty.
[But] regarding the ox of Nergal-aha-iddina which died in the house of Sin-bununi:
If Siyatu did not remove the corpse from the house of Sin-bununi and instead Sin-bununi made a false accusation against Siyatu, then may the man of Nergal-aha-iddina [i.e., Siyatu] be cleared [of wrongdoing by the ordeal] and Sin-bununi be proved guilty.
The record reads almost in note form, so it might be worth a quick review of what we think happened. Nergal-aha-iddina1 was the original owner of an ox, which he loaned to Sin-bununi.2 When Nergal-aha-iddina wanted his ox back, Sin-bununi said the ox had died and that Siyatu,3 Nergal-aha-iddina’s servant, had taken the corpse.
The case described in the tablet is unusual for two reasons. First, the shakannakku was normally a royal proxy but in this case we are told it was the King of Babylon himself, Adad-šuma-usur.4 Second, the judgement is for a trial by water ordeal. Someone is going to be thrown into the river; guilt will be decided by whether the water rejects them or absorbs them.
The tablet contains words, but its interpretation requires knowledge. Jonathan5 was kind enough to let me and my students watch him transliterate the tablet, and as he worked he used books, computer databases, his own expert knowledge and also his sense of what it means to be a human. The suspicion is that Sin-bununi may have sold the ox because his explanation of events – that the ox died and the servant, Siyatu, came, took the body and fed it to a dog – feels like a version of the modern ‘dog ate my homework’ excuse. The case hinges on an accusation, but it’s one person’s word against another.
This judgement was passed over 3,200 years ago but, like a modern case, making it would have involved listening to witness statements and then coming to a decision. The choice of trial by ordeal implies that the witness statements conflicted and the King felt he couldn’t decide on the basis of the evidence. The trial by ordeal passes the decision-making from the shakannakku to the gods; it’s cleromancy with fatal implications. From the translation, it’s not quite clear who’s going in the river … is it Siyatu the servant or Sin-bununi the accuser? My human cynicism suspects it’s the servant that’s going to get wet. Even over 3,000 years later, despite the different cultural landscape, we can still imagine something about the power dynamics at play, and my gut tells me that putting the servant through the ordeal will be the most palatable solution to the King.
Sin-bununi’s story for explaining what happened to the body of the ox reads suspiciously, but while we can speculate about what happened, we can’t know exactly what did happen – there is uncertainty. Even at the time of the trial, the King felt unable to make a decision, so given he wasn’t able to establish the truth so many years ago, we’re unlikely to find it now. This is a cold case, so cold it’s deep frozen, but anyone reading the story can’t help but try to defrost it through the warmth of their human understanding.
We may think we’ve moved beyond the idea of trial by ordeal, but I see a similar trend emerging with our desire to use AI systems for consequential decisions. When humans feel unable to pass judgement they are tempted to pass the decision on to what they believe to be an omniscient entity, but the gremlin of uncertainty means the machine is not omniscient – putting consequential decisions on machines implies that you will be exchanging human error for machine error. That is problematic because the machine can never feel the consequences of those errors as it is not subject to the same vulnerabilities as us. That is why it’s vital the human remains in ultimate control. That’s not to say the human should ignore the machine; rather, we would like the machine to augment our understanding.
See Lawrence (2024) trial of Siyatu p. 338–342, 349–351.
Computers Presumed Correct
One may think that the days of placing our faith in a “trial by ordeal” are in the past. But the computer can also take on the form of a god in the way in which we treat it and its judgments.


Figure:
We can see this presumption as a modern variant of “trial by ordeal” as experienced by Siyatu.
For more details see Bohm et al. (2022).
A Question of Trust
In Baroness Onora O’Neill’s Reeith Lectures from 2002, she raises the challenge of trust. There are many aspects to her arcuments, but one of the key points she makes is that we cannot trust without the notion of duty. O’Neill is bemoaning the substitution of duty with process. The idea is that processes and transparency are supposed to hold us to account by measuring outcomes. But these processes themselves overwhelm decision makers and undermine their professional duty to deliver the right outcome.


Figure: A Question of Trust by Onora O’Neil which examines the nature of trust and its role in society.
Again Univesities are to treat each applicant fairly on the basis of ability and promise, but they are supposed also to admit a socially more representative intake.
There’s no guarantee that the process meets the target.
Onora O’Neill A Question of Trust: Called to Account Reith Lectures 2002 O’Neill (2002)]
O’Neill is speaking in 2002, in the early days of the internet and before social media. Much of her thoughts are even more relevant for today than they were when she spoke. This is because the increased availability of information and machine driven decision-making makes the mistaken premise, that process is an adequate substitute for duty, more apparently plausible. But this undermines what O’Neill calls “intelligent accountability”, which is not accounting by the numbers, but through professional education and institutional safeguards.
See Lawrence (2024) O’Neill, Baroness Onora: ‘A question of trust’ lecture series (2002) p. 352, 363.
Blake’s Newton
William Blake’s rendering of Newton captures humans in a particular state. He is trance-like absorbed in simple geometric shapes. The feel of dreams is enhanced by the underwater location, and the nature of the focus is enhanced because he ignores the complexity of the sea life around him.
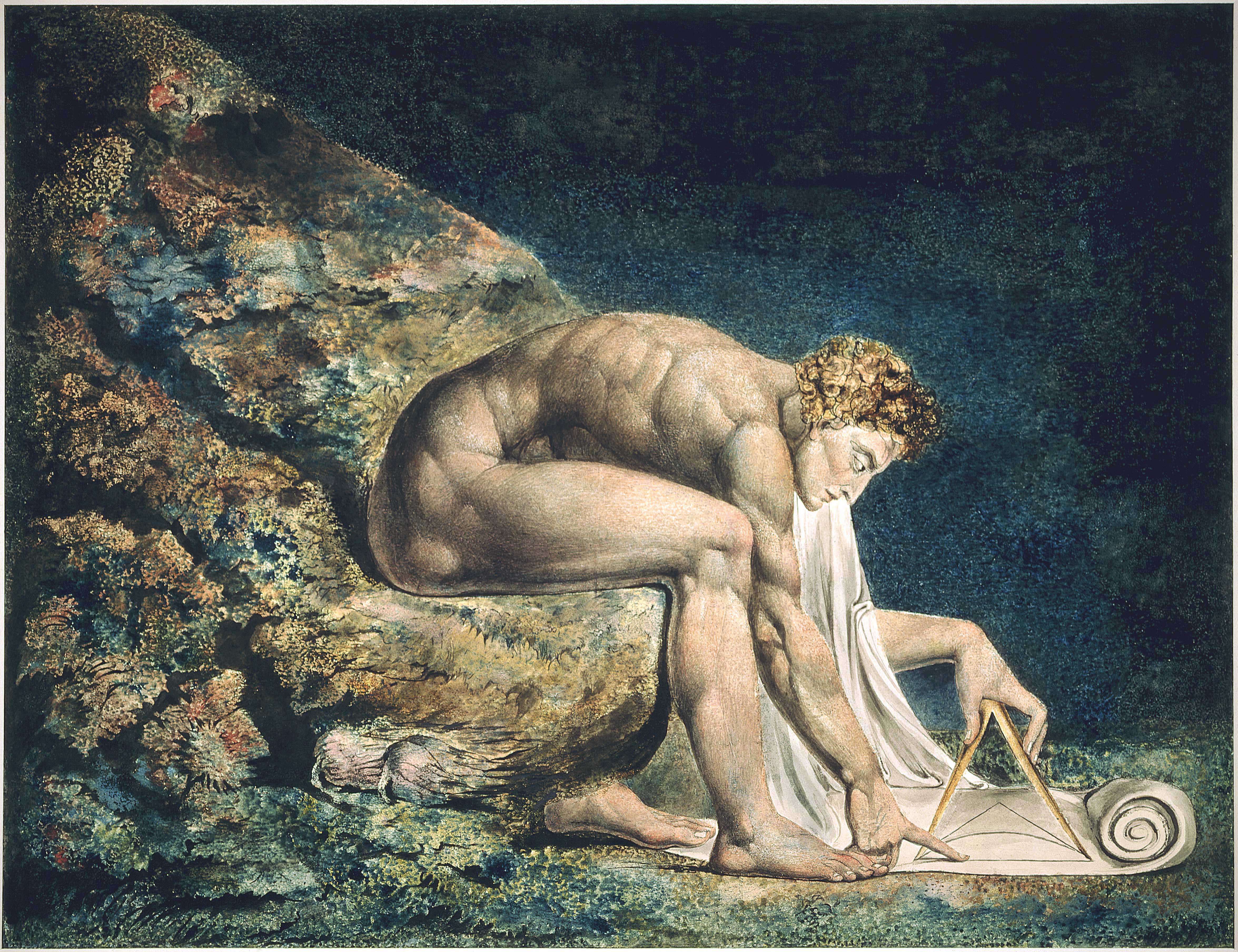


Figure: William Blake’s Newton. 1795c-1805
See Lawrence (2024) Blake, William Newton p. 121–123.
The caption in the Tate Britain reads:
Here, Blake satirises the 17th-century mathematician Isaac Newton. Portrayed as a muscular youth, Newton seems to be underwater, sitting on a rock covered with colourful coral and lichen. He crouches over a diagram, measuring it with a compass. Blake believed that Newton’s scientific approach to the world was too reductive. Here he implies Newton is so fixated on his calculations that he is blind to the world around him. This is one of only 12 large colour prints Blake made. He seems to have used an experimental hybrid of printing, drawing, and painting.
From the Tate Britain
See Lawrence (2024) Blake, William Newton p. 121–123, 258, 260, 283, 284, 301, 306.
The MONIAC
The MONIAC was an analogue computer designed to simulate the UK economy. Analogue comptuers work through analogy, the analogy in the MONIAC is that both money and water flow. The MONIAC exploits this through a system of tanks, pipes, valves and floats that represent the flow of money through the UK economy. Water flowed from the treasury tank at the top of the model to other tanks representing government spending, such as health and education. The machine was initially designed for teaching support but was also found to be a useful economic simulator. Several were built and today you can see the original at Leeds Business School, there is also one in the London Science Museum and one in the Unisversity of Cambridge’s economics faculty.
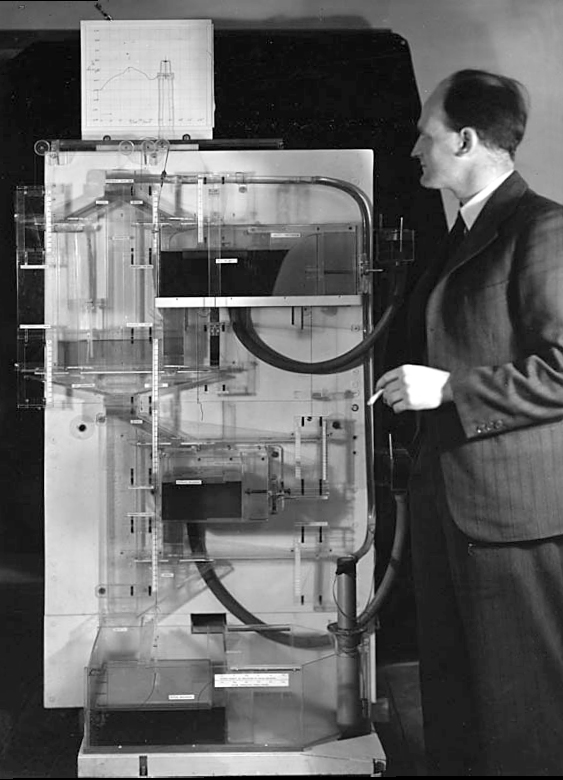

Figure: Bill Phillips and his MONIAC (completed in 1949). The machine is an analogue computer designed to simulate the workings of the UK economy.
See Lawrence (2024) MONIAC p. 232-233, 266, 343.
Human Analogue Machine
Recent breakthroughs in generative models, particularly large language models, have enabled machines that, for the first time, can converse plausibly with other humans.
The Apollo guidance computer provided Armstrong with an analogy when he landed it on the Moon. He controlled it through a stick which provided him with an analogy. The analogy is based in the experience that Amelia Earhart had when she flew her plane. Armstrong’s control exploited his experience as a test pilot flying planes that had control columns which were directly connected to their control surfaces.

Figure: The human analogue machine is the new interface that large language models have enabled the human to present. It has the capabilities of the computer in terms of communication, but it appears to present a “human face” to the user in terms of its ability to communicate on our terms. (Image quite obviously not drawn by generative AI!)
The generative systems we have produced do not provide us with the “AI” of science fiction. Because their intelligence is based on emulating human knowledge. Through being forced to reproduce our literature and our art they have developed aspects which are analogous to the cultural proxy truths we use to describe our world.
These machines are to humans what the MONIAC was the British economy. Not a replacement, but an analogue computer that captures some aspects of humanity while providing advantages of high bandwidth of the machine.
HAM
The Human-Analogue Machine or HAM therefore provides a route through which we could better understand our world through improving the way we interact with machines.

Figure: The trinity of human, data, and computer, and highlights the modern phenomenon. The communication channel between computer and data now has an extremely high bandwidth. The channel between human and computer and the channel between data and human is narrow. New direction of information flow, information is reaching us mediated by the computer. The focus on classical statistics reflected the importance of the direct communication between human and data. The modern challenges of data science emerge when that relationship is being mediated by the machine.
The HAM can provide an interface between the digital computer and the human allowing humans to work closely with computers regardless of their understandin gf the more technical parts of software engineering.

Figure: The HAM now sits between us and the traditional digital computer.
Of course this route provides new routes for manipulation, new ways in which the machine can undermine our autonomy or exploit our cognitive foibles. The major challenge we face is steering between these worlds where we gain the advantage of the computer’s bandwidth without undermining our culture and individual autonomy.
See Lawrence (2024) human-analogue machine (HAMs) p. 343-347, 359-359, 365-368.
Bandwidth vs Complexity
The computer communicates in Gigabits per second, One way of imagining just how much slower we are than the machine is to look for something that communicates in nanobits per second.

|
|||
| bits/min | \(100 \times 10^{-9}\) | \(2,000\) | \(600 \times 10^9\) |

Figure: When we look at communication rates based on the information passing from one human to another across generations through their genetics, we see that computers watching us communicate is roughly equivalent to us watching organisms evolve. Estimates of germline mutation rates taken from Scally (2016).

Figure: Bandwidth vs Complexity.
The challenge we face is that while speed is on the side of the machine, complexity is on the side of our ecology. Many of the risks we face are associated with the way our speed undermines our ecology and the machines speed undermines our human culture.
See Lawrence (2024) Human evolution rates p. 98-99. See Lawrence (2024) Psychological representation of Ecologies p. 323-327.
Conclusions
The atomic human emerges from limitations and vulnerabilities. It is that shared experience that gives individual humans and their institutions the authority to make consequential decisions about other humans that may effect their financial status, their reputation, their health, education or their liberty.
A challenge we face is that of the “sorcerer’s apprentice” where companies have deployed capabilities that they can’t control and that have compromised the nature of the open society.
As future professionals you will need to be able to wield these capabilities and understand their weaknesses to fulfill your role in society.
Thanks!
For more information on these subjects and more you might want to check the following resources.
- book: The Atomic Human
- twitter: @lawrennd
- podcast: The Talking Machines
- newspaper: Guardian Profile Page
- blog: http://inverseprobability.com